A study of the prostate, androgens and sexual activity of male rats
- PMID: 17367532
- PMCID: PMC1845164
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-5-11
A study of the prostate, androgens and sexual activity of male rats
Abstract
Background: The prostate is a sexual gland that produces important substances for the potency of sperm to fertilize eggs within the female reproductive tract, and is under complex endocrine control. Taking advantage of the peculiar behavioral pattern of copulating male rats, we developed experimental paradigms to determine the influence of sexual behavior on the level of serum testosterone, prostate androgen receptors, and mRNA for androgen receptors in male rats displaying up to four consecutive ejaculations.
Methods: The effect of four consecutive ejaculations was investigated by determining levels of (i) testosterone in serum by solid phase RIA, (ii) androgen receptors at the ventral prostate with Western Blots, and (iii) androgen receptors-mRNA with RT-PCR. Data were analyzed with a one-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc application of Dunnett's test if required.
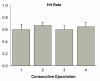
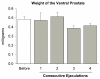
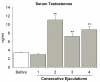
Results: The constant execution of sexual behavior did not produce any change in the weight of the ventral prostate. Serum testosterone increased after the second ejaculation, and remained elevated even after four ejaculations. The androgen receptor at the ventral prostate was higher after the first to third ejaculations, but returned suddenly to baseline levels after the fourth ejaculation. The level of mRNA increased after the first ejaculation, continued to increase after the second, and reached the highest peak after the third ejaculation; however, it returned suddenly to baseline levels after the fourth ejaculation.
Conclusion: Four consecutive ejaculations by sexually experienced male rats had important effects on the physiological responses of the ventral prostate. Fast responses were induced as a result of sexual behavior that involved an increase and decrease in androgen receptors after one and four ejaculations, respectively. However, a progressive response was observed in the elevation of mRNA for androgen receptors, which also showed a fast decrease after four ejaculations. All of these changes with the prostate gland occurred in the presence of a sustained elevation of testosterone in the serum that started after two ejaculations. A consideration of these fast-induced changes suggests that the nerve supply plays a key role in prostate physiology during the sexual behavior of male rats.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of spinal cord injury on the status of messenger ribonucleic acid for TRPM 2 and androgen receptor in the prostate of the rat.J Androl. 1997 May-Jun;18(3):250-6. J Androl. 1997. PMID: 9203052
-
Correlation of prolactin levels and PRL-receptor expression with Stat and Mapk cell signaling in the prostate of long-term sexually active rats.Physiol Behav. 2015 Jan;138:188-92. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.10.036. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 25446202
-
Relationship between sexual satiety and brain androgen receptors.Neuroendocrinology. 2007;85(1):16-26. doi: 10.1159/000099250. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Neuroendocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17268169
-
Neurohormonal bases of male sexual behavior.Int Rev Physiol. 1977;13:225-54. Int Rev Physiol. 1977. PMID: 321383 Review. No abstract available.
-
[Acne vulgaris: endocrine aspects].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006 Jun 10;150(23):1281-5. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006. PMID: 16821451 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Using Dendritic Cells in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 21;26(10):4939. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104939. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fos expression at the cerebellum following non-contact arousal and mating behavior in male rats.Physiol Behav. 2008 Jan 28;93(1-2):357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 17936859 Free PMC article.
-
Increased de novo glutathione production enhances sexual dysfunctions in rats subjected to paradoxical sleep deprivation.JBRA Assist Reprod. 2021 Apr 27;25(2):215-222. doi: 10.5935/1518-0557.20200070. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33150783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fielder TJ, Peacock NR, McGivern RF, Swerdloff RS, Bhasin S. Testosterone dose-dependency of sexual and nonsexual behaviors in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist-treated male rat. J Androl. 1989;10:167–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

