Tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU6668 represses chondrosarcoma growth via antiangiogenesis in vivo
- PMID: 17367541
- PMCID: PMC1832206
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-49
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor SU6668 represses chondrosarcoma growth via antiangiogenesis in vivo
Abstract
Background: As chondrosarcomas are resistant to chemotherapy and ionizing radiation, therapeutic options are limited. Radical surgery often cannot be performed. Therefore, additional therapies such as antiangiogenesis represent a promising strategy for overcoming limitations in chondrosarcoma therapy. There is strong experimental evidence that SU6668, an inhibitor of the angiogenic tyrosine kinases Flk-1/KDR, PDGFRbeta and FGFR1 can induce growth inhibition of various primary tumors. However, the effectiveness of SU6668 on malignant primary bone tumors such as chondrosarcomas has been rarely investigated. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of SU6668 on chondrosarcoma growth, angiogenesis and microcirculation in vivo.
Methods: In 10 male severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice, pieces of SW1353 chondrosarcomas were implanted into a cranial window preparation where the calvaria serves as the site for the orthotopic implantation of bone tumors. From day 7 after tumor implantation, five animals were treated with SU6668 (250 mg/kg body weight, s.c.) at intervals of 48 hours (SU6668), and five animals with the equivalent amount of the CMC-based vehicle (Control). Angiogenesis, microcirculation, and growth of SW 1353 tumors were analyzed by means of intravital microscopy.
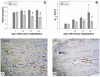
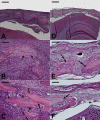
Results: SU6668 induced a growth arrest of chondrosarcomas within 7 days after the initiation of the treatment. Compared to Controls, SU6668 decreased functional vessel density and tumor size, respectively, by 37% and 53% on day 28 after tumor implantation. The time course of the experiments demonstrated that the impact on angiogenesis preceded the anti-tumor effect. Histological and immunohistochemical results confirmed the intravital microscopy findings.
Conclusion: SU6668 is a potent inhibitor of chondrosarcoma tumor growth in vivo. This effect appears to be induced by the antiangiogenic effects of SU6668, which are mediated by the inhibition of the key angiogenic receptor tyrosine kinases Flk-1/KDR, PDGFRbeta and FGFR1. The experimental data obtained provide rationale to further develop the strategy of the use of the angiogenesis inhibitor SU6668 in the treatment of chondrosarcomas in addition to established therapies such as surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The selective Cox-2 inhibitor Celecoxib suppresses angiogenesis and growth of secondary bone tumors: an intravital microscopy study in mice.BMC Cancer. 2006 Jan 12;6:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-9. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16409625 Free PMC article.
-
Combined antiangiogenic and immune therapy of prostate cancer.Angiogenesis. 2005;8(1):13-23. doi: 10.1007/s10456-005-2893-y. Angiogenesis. 2005. PMID: 16132614
-
Combined therapy of local and metastatic 4T1 breast tumor in mice using SU6668, an inhibitor of angiogenic receptor tyrosine kinases, and the immunostimulator B7.2-IgG fusion protein.Cancer Res. 2002 Oct 15;62(20):5727-35. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12384531
-
SU6668, a multitargeted angiogenesis inhibitor.Cancer J. 2001 Nov-Dec;7 Suppl 3:S134-8. Cancer J. 2001. PMID: 11779084 Review.
-
Distribution, metabolism, and excretion of the anti-angiogenic compound SU5416.Toxicol In Vitro. 2006 Mar;20(2):154-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2005.06.047. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006. PMID: 16321501 Review.
Cited by
-
New clinically relevant, orthotopic mouse models of human chondrosarcoma with spontaneous metastasis.Cancer Cell Int. 2010 Jun 28;10:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-10-20. Cancer Cell Int. 2010. PMID: 20584302 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced chondrosarcomas: role of chemotherapy and survival.Ann Oncol. 2013 Nov;24(11):2916-22. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt374. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24099780 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Therapy for Chondrosarcoma.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Feb;23(2):199-209. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-00951-7. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35190971 Review.
-
Survival and prognostic factors in chondrosarcoma: results in 115 patients with long-term follow-up.Acta Orthop. 2011 Dec;82(6):749-55. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2011.636668. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Acta Orthop. 2011. PMID: 22066552 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Benefit of Pazopanib in a Patient with Metastatic Chondrosarcoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Front Oncol. 2018 Mar 1;8:45. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00045. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29546033 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

