The utility of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation in a United States referral population
- PMID: 17368240
- PMCID: PMC1931510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2006.12.005
The utility of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation in a United States referral population
Abstract
Background & aims: The percentage of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive (alpha)-fetoprotein (AFP-L3%) is proposed as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We evaluated the utility of AFP-L3% for diagnosis of HCC in a US referral population.
Methods: This retrospective study included 272 patients: 166 with HCC and 106 with benign liver disease (chronic liver disease, 77; benign liver mass, 29). The AFP-L3% was measured using a clinical auto-analyzer.
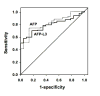
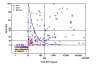
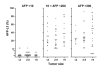
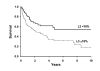
Results: The AFP-L3% is not reported for a total alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) less than 10 ng/mL, and all patients with an AFP greater than 200 ng/mL had HCC; thus the AFP-L3% was noninformative for these patients. In patients with a total AFP of 10-200 ng/mL, an AFP-L3% greater than 10% had a sensitivity of 71% and a specificity of 63% for diagnosis of HCC. An AFP-L3% greater than 35% had a reduced sensitivity of 33%, but an increased specificity of 100%. The high specificity of the AFP-L3% cut-off of 35% allowed the confident diagnosis of an additional 10% of HCCs not diagnosed using an AFP cut-off of 200 ng/mL. After adjustment for AFP level, no association was observed between AFP-L3% and tumor size, stage, vascular invasion, grade, or survival.
Conclusions: Patients with indeterminate total AFP values of 10-200 ng/mL present a diagnostic dilemma. We found that an AFP-L3% greater than 35% has 100% specificity for HCC in these patients. AFP-L3%, used in combination with AFP, may be a clinically useful adjunct marker for the diagnosis of HCC.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Clinical utility of lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: evaluation in a Thai referral population.J Med Assoc Thai. 2009 Mar;92 Suppl 2:S49-56. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009. PMID: 19562986
-
Diagnostic value of AFP-L3 and PIVKA-II in hepatocellular carcinoma according to total-AFP.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan 21;19(3):339-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i3.339. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23372355 Free PMC article.
-
Lens culinaris-agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein is a prognostic biomarker in atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep 1;37(9):1055-1062. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002979. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40359294
-
Alpha-fetoprotein-L3 in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Oct 21;425:212-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23954771
-
Highly sensitive Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive α-fetoprotein: a new tool for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncology. 2011;81 Suppl 1:61-5. doi: 10.1159/000333263. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Oncology. 2011. PMID: 22212938 Review.
Cited by
-
Redefining HCC Surveillance in India: A Call for Innovative and Inclusive Strategies.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 Nov-Dec;14(6):101474. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.101474. Epub 2024 Jun 25. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39108278 Review.
-
Glycan array analysis of Pholiota squarrosa lectin and other fucose-oriented lectins.Glycobiology. 2021 May 3;31(4):459-476. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa093. Glycobiology. 2021. PMID: 33021632 Free PMC article.
-
Capitalizing glycomic changes for improved biomarker-based cancer diagnostics.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023;4(3):366-395. doi: 10.37349/etat.2023.00140. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2023. PMID: 37455827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of FOXO6 is Associated With Oxidative Stress Level and Predicts the Prognosis in Hepatocellular Cancer: A Comparative Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(21):e3708. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003708. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27227932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016 Apr;12(4):252-5. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016. PMID: 27231457 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ, McGlynn KA. The continuing increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: an update. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:817–23. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Mason AC, Key C. Trends in survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma between 1977 and 1996 in the United States. Hepatology. 2001;33:62–5. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Siegel AB, Davila JA, Shaib YH, Cayton-Woody M, McBride R, McGlynn KA. Treatment and outcomes of treating of hepatocellular carcinoma among Medicare recipients in the United States: a population-based study. J Hepatol. 2006;44:158–66. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi K, Kumada T, Nakano S, Takeda I, Sugiyama K, Kiriyama S, Sone Y, Miyata A, Shimizu H, Satomura S. Usefulness of measurement of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein as a marker of prognosis and recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94:3028–33. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K, Tanaka M, Kanazawa N, Nagashima J, Satomura S, Kinoshita H, Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Kojiro M. Evaluation of curability and prediction of prognosis after surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma by lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein. Int J Oncol. 1999;14:265–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

