Serotonin receptor involvement in effects of restraint on female rat lordosis behavior
- PMID: 17368527
- PMCID: PMC2043475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.02.007
Serotonin receptor involvement in effects of restraint on female rat lordosis behavior
Abstract
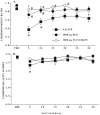
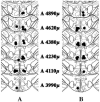
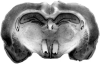
Ovariectomized Fischer (CDF-344) rats, with bilateral cannulae in the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH) near the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN), were used to test the hypothesis that serotonin receptors in the VMN contribute to the lordosis-inhibiting effects of mild restraint. Rats were hormonally primed with 10 microg estradiol benzoate (EB) followed 48 h later with sesame seed oil. Four to six hours later (during the dark portion of the light-dark cycle), rats were pretested for sexual behavior. Thereafter, they were infused with saline, 2 microg of the serotonin (5-HT) 2 receptor agonist, (+/-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane HCl (DOI), or 1 microg of the 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist, N-{2[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl}-N-(2-pyridinyl) cyclohexanecarboxamide trihydrochloride (WAY100635). After a 5 min restraint, rats were tested for sexual receptivity. Rats infused with saline showed a significant decline in lordosis behavior after restraint. Infusion with either DOI or WAY100635 attenuated these effects of restraint. These findings extend earlier observations that the lordosis-disruptive effects of mild restraint include activation of 5-HT(1A) receptors in the VMN and are the first to implicate VMN 5-HT(2) receptors in protection against mild restraint.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progesterone reduces the effect of the serotonin 1B/1D receptor antagonist, GR 127935, on lordosis behavior.Horm Behav. 2009 Jan;55(1):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.09.011. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Horm Behav. 2009. PMID: 18952090 Free PMC article.
-
Restraint accentuates the effects of 5-HT2 receptor antagonists and a 5-HT1A receptor agonist on lordosis behavior.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003 Aug;76(1):63-73. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(03)00194-1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003. PMID: 13679218
-
WAY100635 and female rat lordosis behavior.Brain Res. 2004 Jul 9;1013(2):260-3. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.013. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15193537
-
5-HT2C receptor involvement in female rat lordosis behavior.Brain Res. 1999 Apr 17;825(1-2):146-51. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01159-2. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10216181
-
Progesterone attenuates the effect of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT, and of mild restraint on lordosis behavior.Brain Res. 2003 Jun 6;974(1-2):202-11. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02581-2. Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12742638
Cited by
-
Prior hormonal treatment, but not sexual experience, reduces the negative effects of restraint on female sexual behavior.Behav Brain Res. 2014 Feb 1;259:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.10.031. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24172220 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone reduces the effect of the serotonin 1B/1D receptor antagonist, GR 127935, on lordosis behavior.Horm Behav. 2009 Jan;55(1):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.09.011. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Horm Behav. 2009. PMID: 18952090 Free PMC article.
-
RU486 blocks effects of allopregnanolone on the response to restraint stress.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 Jan;103(3):568-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.09.024. Epub 2012 Oct 6. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013. PMID: 23046854 Free PMC article.
-
Tropisetron increases the inhibitory effect of mild restraint on lordosis behavior of hormonally primed, ovariectomized rats.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Jun 1;219(2):221-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21238491 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms responsible for progesterone's protection against lordosis-inhibiting effects of restraint I. Role of progesterone receptors.Horm Behav. 2011 Jul;60(2):219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.05.006. Epub 2011 May 20. Horm Behav. 2011. PMID: 21635894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bethea CL, Lu NZ, Gundlah C, Streicher JM. Diverse actions of ovarian steroids in the serotonin neural system. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2002;23(1):41–100. - PubMed
-
- Campbell GA, Kurcz M, Marshall S, Meites J. Effects of starvation in rats on serum levels of follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, thyrotropin, growth hormone and prolactin; response to LH-releasing hormone and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Endocrinology. 1977;100(2):580–7. - PubMed
-
- Cyr M, Bosse R, Di Paolo T. Gonadal hormones modulate 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptors: emphasis on the rat frontal cortex. Neuroscience. 1998;83(3):829–36. - PubMed
-
- Dobson H, Ghuman S, Prabhakar S, Smith R. A conceptual model of the influence of stress on female reproduction. Reproduction. 2003;125(2):151–63. - PubMed
-
- Farmer CJ, Isakson TR, Coy DJ, Renner KJ. In vivo evidence for progesterone dependent decreases in serotonin release in the hypothalamus and midbrain central grey: relation to the induction of lordosis. Brain Res. 1996;711(12):84–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

