Flumazenil-sensitive dose-related physical dependence in planarians produced by two benzodiazepine and one non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepine-receptor agonists
- PMID: 17368613
- PMCID: PMC2697456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.006
Flumazenil-sensitive dose-related physical dependence in planarians produced by two benzodiazepine and one non-benzodiazepine benzodiazepine-receptor agonists
Abstract
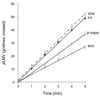
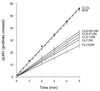
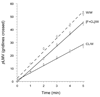
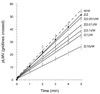
Two benzodiazepine (midazolam and clorazepate) and one non-benzodiazepine (zolpidem) benzodiazepine-receptor agonists produced dose-related physical dependence, as evidenced by abstinence-induced decrease in planarian locomotor velocity (pLMV) when drug-exposed planarians were placed into drug-free water, but not when they were placed into drug-containing water (i.e., an abstinence-induced withdrawal, since the effect was only obtained in the removal of drug and not in the continued presence of drug). We have previously shown that the decrease in pLMV is associated with specific and transient withdrawal signs. In the present study, the selective benzodiazepine-receptor antagonist flumazenil significantly antagonized (P<0.05), by co-application, the ability of each agonist to produce the withdrawal. These results: (1) suggest that benzodiazepine-receptor agonists, for two different chemical categories, produce dose-related physical dependence manifested as abstinence-induced withdrawal in this simple and convenient model, and (2) in the absence of cloning or radioligand binding literature, suggest a possible specific interaction site (receptor?) for these compounds in planarians.
Figures



References
-
- Algeri S, Carolei A, Ferretti P, Gallone C, Palladini G, Venturini G. Effects of dopaminergic agents on monoamine levels and motor behaviour in Planaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1983;74C:27–29. - PubMed
-
- Buhr A, Baur R, Sigel E. Subtle changes in residue 77 of the gamma subunit of α1β2γ2 GABAA receptors drastically alter the affinity for ligands of the benzodiazepine binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:11799–11804. - PubMed
-
- Bateson AN. Basic pharmacologic mechanisms involved in benzodiazepine tolerance and withdrawal. Curr. Pharmaceut. Design. 2002;8:5–21. - PubMed
-
- Begg DP, Hallam KT, Norman TR. Attenuation of benzodiazepine withdrawal anxiety in the rat by serotonin antagonists. Behav. Brain Res. 2005;161:286–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

