Septum-localized protein required for filament integrity and diazotrophy in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120
- PMID: 17369306
- PMCID: PMC1913322
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00085-07
Septum-localized protein required for filament integrity and diazotrophy in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120
Abstract
Heterocysts, formed when filamentous cyanobacteria, such as Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120, are grown in the absence of combined nitrogen, are cells that are specialized in fixing atmospheric nitrogen (N(2)) under oxic conditions and that transfer fixed nitrogen to the vegetative cells of the filament. Anabaena sp. mutants whose sepJ gene (open reading frame alr2338 of the Anabaena sp. genome) was affected showed filament fragmentation and arrested heterocyst differentiation at an early stage. In a sepJ insertional mutant, a layer similar to a heterocyst polysaccharide layer was formed, but the heterocyst-specific glycolipids were not synthesized. The sepJ mutant did not exhibit nitrogenase activity even when assayed under anoxic conditions. In contrast to proheterocysts produced in the wild type, those produced in the sepJ mutant still divided. SepJ is a multidomain protein whose N-terminal region is predicted to be periplasmic and whose C-terminal domain resembles an export permease. Using a green fluorescent protein translationally fused to the carboxyl terminus of SepJ, we observed that in mature heterocysts and vegetative cells, the protein is localized at the intercellular septa, and when cell division starts, it is localized in a ring whose position is similar to that of a Z ring. SepJ is a novel composite protein needed for filament integrity, proper heterocyst development, and diazotrophic growth.
Figures


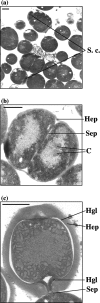


Similar articles
-
Functional Dependence between Septal Protein SepJ from Anabaena sp. Strain PCC 7120 and an Amino Acid ABC-Type Uptake Transporter.J Bacteriol. 2015 Aug;197(16):2721-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.00289-15. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26078444 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SepJ alters septal morphology and heterocyst pattern regulated by diffusible signals in Anabaena.Mol Microbiol. 2016 Sep;101(6):968-81. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13436. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Mol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27273832
-
Functional dissection of the three-domain SepJ protein joining the cells in cyanobacterial trichomes.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Feb;79(4):1077-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07508.x. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21299655
-
The periplasmic and cytoplasmic faces of septal protein SepJ from filamentous cyanobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2025 May 22;207(5):e0048824. doi: 10.1128/jb.00488-24. Epub 2025 Mar 31. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40162858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cell wall in heterocyst formation by Anabaena sp. PCC 7120.J Basic Microbiol. 2009 Feb;49(1):5-24. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200800300. J Basic Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19253332 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Dependence between Septal Protein SepJ from Anabaena sp. Strain PCC 7120 and an Amino Acid ABC-Type Uptake Transporter.J Bacteriol. 2015 Aug;197(16):2721-30. doi: 10.1128/JB.00289-15. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26078444 Free PMC article.
-
Specific mutations in the permease domain of septal protein SepJ differentially affect functions related to multicellularity in the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena.Microb Cell. 2018 Oct 16;5(12):555-565. doi: 10.15698/mic2018.12.661. Microb Cell. 2018. PMID: 30533420 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial solutions to multicellularity: a tale of biofilms, filaments and fruiting bodies.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014 Feb;12(2):115-24. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3178. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24384602 Review.
-
Requirement of Fra proteins for communication channels between cells in the filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 11;112(32):E4458-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512232112. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26216997 Free PMC article.
-
The amt gene cluster of the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120.J Bacteriol. 2008 Oct;190(19):6534-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00613-08. Epub 2008 Aug 8. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18689479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

