Editing modifies the GABA(A) receptor subunit alpha3
- PMID: 17369310
- PMCID: PMC1852825
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.349107
Editing modifies the GABA(A) receptor subunit alpha3
Abstract
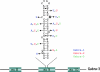
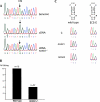
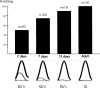
Adenosine to inosine (A-to-I) pre-mRNA editing by the ADAR enzyme family has the potential to increase the variety of the proteome. This editing by adenosine deamination is essential in mammals for a functional brain. To detect novel substrates for A-to-I editing we have used an experimental method to find selectively edited sites and combined it with bioinformatic techniques that find stem-loop structures suitable for editing. We present here the first verified editing candidate detected by this screening procedure. We show that Gabra-3, which codes for the alpha3 subunit of the GABA(A) receptor, is a substrate for editing by both ADAR1 and ADAR2. Editing of the Gabra-3 mRNA recodes an isoleucine to a methionine. The extent of editing is low at birth but increases with age, reaching close to 100% in the adult brain. We therefore propose that editing of the Gabra-3 mRNA is important for normal brain development.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
