In silico screening of archaeal tRNA-encoding genes having multiple introns with bulge-helix-bulge splicing motifs
- PMID: 17369313
- PMCID: PMC1852824
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.309507
In silico screening of archaeal tRNA-encoding genes having multiple introns with bulge-helix-bulge splicing motifs
Abstract
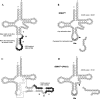
In archaeal species, several transfer RNA genes have been reported to contain endogenous introns. Although most of the introns are located at anticodon loop regions between nucleotide positions 37 and 38, a number of introns at noncanonical sites and six cases of tRNA genes containing two introns have also been documented. However, these tRNA genes are often missed by tRNAscan-SE, the software most widely used for the annotation of tRNA genes. We previously developed SPLITS, a computational tool to identify tRNA genes containing one intron at a noncanonical position on the basis of its discriminative splicing motif, but the software was limited in the detection of tRNA genes with multiple introns at noncanonical sites. In this study, we initially updated the system as SPLITSX in order to correctly predict known tRNA genes as well as novel ones with multiple introns. By a comprehensive search for tRNA genes in 29 archaeal genomes using SPLITSX, we listed 43 novel candidates that contain introns at noncanonical sites. As a result, 15 contained two introns and three contained three introns within the respective putative tRNA genes. Moreover, the candidates completely complemented all the codons of two archaeal species of uncultured methanogenic archaeon, RC-I and Thermofilum pendens Hrk 5, with novel candidates that were not detectable by tRNAscan-SE alone.
Figures


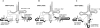
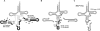
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of archaeal tRNA genes reveals rapid increase of tRNA introns in the order thermoproteales.Mol Biol Evol. 2008 Dec;25(12):2709-16. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn216. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Mol Biol Evol. 2008. PMID: 18832079
-
SPLITS: a new program for predicting split and intron-containing tRNA genes at the genome level.In Silico Biol. 2006;6(5):411-8. In Silico Biol. 2006. PMID: 17274770
-
Large-scale tRNA intron transposition in the archaeal order Thermoproteales represents a novel mechanism of intron gain.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 Oct;27(10):2233-43. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq111. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20430862
-
Archaeal introns: splicing, intercellular mobility and evolution.Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Sep;22(9):326-31. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(97)01113-4. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997. PMID: 9301331 Review.
-
[Intron and pre-mRNA splicing of bacteria and Archaea].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2002 Jun;47(7):833-6. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2002. PMID: 12058480 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of highly-disrupted tRNA genes in nuclear genome of the red alga, Cyanidioschyzon merolae 10D.Sci Rep. 2013;3:2321. doi: 10.1038/srep02321. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23900518 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitochondrial Genomes of a Myxozoan Genus Kudoa Are Extremely Divergent in Metazoa.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132030. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26148004 Free PMC article.
-
On origin of genetic code and tRNA before translation.Biol Direct. 2011 Feb 22;6:14. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-6-14. Biol Direct. 2011. PMID: 21342520 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence of a mesophilic hydrogenotrophic methanogen Methanocella paludicola, the first cultivated representative of the order Methanocellales.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022898. Epub 2011 Jul 29. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829548 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and roles of (t)RNA ligases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(16):2657-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0944-2. Epub 2012 Mar 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22426497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Daniels, C.J., Gupta, R., Doolittle, W.F. Transcription and excision of a large intron in the tRNATrp gene of an archaebacterium, Halobacterium volcanii. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:3132–3134. - PubMed
-
- Datta, P.K., Hawkins, L.K., Gupta, R. Presence of an intron in elongator methionine-tRNA of Halobacterium volcanii. Can. J. Microbiol. 1989;35:189–194. - PubMed
-
- Fichant, G.A., Burks, C. Identifying potential tRNA genes in genomic DNA sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 1991;220:659–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
