Sterol-rich plasma membrane domains in fungi
- PMID: 17369440
- PMCID: PMC1899238
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00008-07
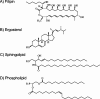
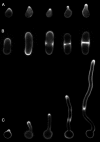
Sterol-rich plasma membrane domains in fungi
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

