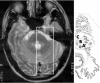
Isolated mediotegmental lesion causing narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: a case evidencing a common pathway in narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder
- PMID: 17369596
- PMCID: PMC2077786
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.099515
Isolated mediotegmental lesion causing narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder: a case evidencing a common pathway in narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder
Abstract
Narcolepsy is usually an idiopathic disorder, often with a genetic predisposition. Symptomatic cases have been described repeatedly, often as a consequence of hypothalamic lesions. Conversely, REM (rapid eye movement) sleep behaviour disorder (RBD) is usually a secondary disorder, often due to degenerative brain stem disorders or narcolepsy. The case of a hitherto healthy man is presented, who simultaneously developed narcolepsy and RBD as the result of an acute focal inflammatory lesion in the dorsomedial pontine tegmentum in the presence of normal cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin-1 levels and in the absence of human lymphocyte antigen haplotypes typically associated with narcolepsy and RBD (DQB1*0602, DQB1*05). This first observation of symptomatic narcolepsy with RBD underlines the importance of the mediotegmental pontine area in the pathophysiology of both disorders, even in the absence of a detectable hypocretin deficiency and a genetic predisposition.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Comment in
-
Towards a common pathway for narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;78(4):331-2. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.106401. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17369587 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder in patients with narcolepsy is associated with hypocretin-1 deficiency.Brain. 2010 Feb;133(Pt 2):568-79. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp320. Epub 2010 Feb 3. Brain. 2010. PMID: 20129934
-
Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder and rapid eye movement sleep without atonia in narcolepsy.Sleep Med. 2013 Aug;14(8):775-81. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2012.10.006. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 23219054
-
Cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin levels are normal in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder.Eur J Neurol. 2010 Aug;17(8):1105-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.02954.x. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Eur J Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20113337
-
REM sleep behavior disorder in narcolepsy: A secondary form or an intrinsic feature?Sleep Med Rev. 2020 Apr;50:101254. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2019.101254. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Sleep Med Rev. 2020. PMID: 31931470 Review.
-
Symptomatic narcolepsy, cataplexy and hypersomnia, and their implications in the hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin system.Sleep Med Rev. 2005 Aug;9(4):269-310. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2005.03.004. Sleep Med Rev. 2005. PMID: 16006155 Review.
Cited by
-
The anatomical, cellular and synaptic basis of motor atonia during rapid eye movement sleep.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 1;594(19):5391-414. doi: 10.1113/JP271324. Epub 2016 Jul 3. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27060683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morbidities in rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder.Sleep Med. 2013 Aug;14(8):782-7. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2012.11.002. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 23375425 Free PMC article.
-
Towards a common pathway for narcolepsy and rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007 Apr;78(4):331-2. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.106401. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17369587 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of REM sleep without atonia in patients with narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia using AASM scoring manual criteria.J Clin Sleep Med. 2013 Jul 15;9(7):675-80. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.2836. J Clin Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 23853561 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical Location of the Mesencephalic Locomotor Region and Its Possible Role in Locomotion, Posture, Cataplexy, and Parkinsonism.Front Neurol. 2015 Jun 24;6:140. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00140. eCollection 2015. Front Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26157418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassetti C, Aldrich M S, Quint D J. MRI findings in narcolepsy. Sleep 199720630–631. - PubMed
-
- Nishino S, Kanbayashi T. Symptomatic narcolepsy, cataplexy and hypersomnia, and their implications in the hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin system. Sleep Med Rev 20059269–310. - PubMed
-
- Jouvet M, Delorme F. Locus coeruleus et sommeil paradoxal. C R Soc Biol 1965159895–899.
-
- Schenck C H, Mahowald M W. Motor dyscontrol in narcolepsy: rapid‐eye‐movement (REM) sleep without atonia and REM sleep behavior disorder. Ann Neurol 1992323–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical