Neuropilin-1 promotes human glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine pathway
- PMID: 17369861
- PMCID: PMC2846324
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210348
Neuropilin-1 promotes human glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine pathway
Abstract
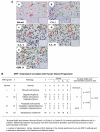
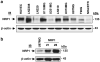
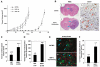
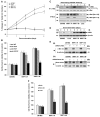
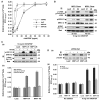
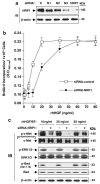
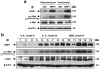
Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) functions as a coreceptor through interaction with plexin A1 or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor during neuronal development and angiogenesis. NRP1 potentiates the signaling pathways stimulated by semaphorin 3A and VEGF-A in neuronal and endothelial cells, respectively. In this study, we investigate the role of tumor cell-expressed NRP1 in glioma progression. Analyses of human glioma specimens (WHO grade I-IV tumors) revealed a significant correlation of NRP1 expression with glioma progression. In tumor xenografts, overexpression of NRP1 by U87MG gliomas strongly promoted tumor growth and angiogenesis. Overexpression of NRP1 by U87MG cells stimulated cell survival through the enhancement of autocrine hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF)/c-Met signaling. NRP1 not only potentiated the activity of endogenous HGF/SF on glioma cell survival but also enhanced HGF/SF-promoted cell proliferation. Inhibition of HGF/SF, c-Met and NRP1 abrogated NRP1-potentiated autocrine HGF/SF stimulation. Furthermore, increased phosphorylation of c-Met correlated with glioma progression in human glioma biopsies in which NRP1 is upregulated and in U87MG NRP1-overexpressing tumors. Together, these data suggest that tumor cell-expressed NRP1 promotes glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine c-Met signaling pathway, in addition to enhancing angiogenesis, suggesting a novel mechanism of NRP1 in promoting human glioma progression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual effects of targeting neuropilin-1 in lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma: inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):C1150-C1161. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00511.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39250819
-
Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 act as coreceptors, potentiating proangiogenic activity.Blood. 2008 Feb 15;111(4):2036-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-04-084269. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18065694
-
Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor (SF/HGF) content and function in human gliomas.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1999 Aug-Oct;17(5-6):517-30. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(99)00008-8. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10571413 Review.
-
Neuropilin-1 signaling through p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylation is essential for growth factor-dependent migration of glioma and endothelial cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Mar;31(6):1174-85. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00903-10. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21245381 Free PMC article.
-
Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis.Neuro Oncol. 2005 Oct;7(4):436-51. doi: 10.1215/S1152851705000050. Neuro Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16212809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropilin-1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer.J Cancer. 2021 Apr 30;12(12):3648-3659. doi: 10.7150/jca.52851. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33995640 Free PMC article.
-
The role of semaphorins and their receptors in gliomas.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:902854. doi: 10.1155/2012/902854. Epub 2012 Sep 23. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 23050142 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-200c sensitizes Olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells by targeting Neuropilin 1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jan 2;39(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1490-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31898520 Free PMC article.
-
The Nervous System Development Regulator Neuropilin-1 as a Potential Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Brain Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4922. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204922. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary epithelial neuropilin-1 deletion enhances development of cigarette smoke-induced emphysema.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Sep 1;180(5):396-406. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200809-1483OC. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19520907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abounader R, Lal B, Luddy C, Koe G, Davidson B, Rosen EM, et al. In vivo targeting of SF/HGF and c-met expression via U1snRNA/ribozymes inhibits glioma growth and angiogenesis and promotes apoptosis. FASEB J. 2002;16:108–110. - PubMed
-
- Bachelder RE, Lipscomb EA, Lin X, Wendt MA, Chadborn NH, Eickholt BJ, et al. Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5230–5233. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Tessier-Lavigne M. Neuropilins as Semaphorin receptors: in vivo functions in neuronal cell migration and axon guidance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:13–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

