Serum level of arginine-vasopressin influences the prognosis of extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 17370088
- PMCID: PMC12160913
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-007-0196-y
Serum level of arginine-vasopressin influences the prognosis of extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to elucidate the influence of serum arginine-vasopressin (AVP) level on prognosis of extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC).
Methods: We retrospectively investigated the clinical records of 163 patients with ED-SCLC, who were admitted to Okayama University Hospital or National Shikoku Cancer Center Hospital. The influence of 14 pretreatment variables on survival was analyzed.
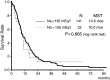
Results: In a multivariate analysis of 163 patients, elevation of serum LDH level (P = 0.028) and poor performance status (PS > or = 2, P = 0.002) were independent poor prognostic factors. In 34 patients whose serum AVP levels were available, high serum AVP level was related to the poor prognosis (P < 0.001). The serum-sodium level did not affect the survival. Median serum level of osmotic pressure in 34 patients was normal (284.9 mOsm/kg), although, serum osmotic pressure was low in four of six patients with high serum AVP level. In all patients with high serum AVP level, serum LDH level was elevated.
Conclusions: The data from the current study suggested that serum LDH level and PS were the poor prognostic factors for ED-SCLC. But we additionally identified the prognostic significance of serum AVP level, which may be a more useful factor than serum-sodium level.
Figures


References
-
- Albain KS, Crowley JJ, LeBlanc M, Livingston RB (1990) Determinants of improved outcome in small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of the 2,580-patient Southwest Oncology Group database. J Clin Oncol 8:1563–1574 - PubMed
-
- American Joint Committee on Cancer (2002) Lung, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 6th edn. Springer, New York, pp 167–177
-
- Bliss DP Jr, Battey JF, Linnoila RI, Birrer MJ, Gazdar AF, Johnson BE (1990) Expression of the atrial natriuretic factor gene in small cell lung cancer tumors and tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:305–310 - PubMed
-
- Boring CC, Squires TS, Tong T, Montgomery S (1994) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 44:7–26 - PubMed
-
- Byhardt RW, Hartz A, Libnoch JA, Hansen R, Cox JD (1986) Prognostic influence of TNM staging and LDH levels in small cell carcinoma of the lung (SCLC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 12:771–777 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

