Modelling the 5-year cost effectiveness of tiotropium, salmeterol and ipratropium for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Spain
- PMID: 17370096
- PMCID: PMC1913175
- DOI: 10.1007/s10198-007-0039-4
Modelling the 5-year cost effectiveness of tiotropium, salmeterol and ipratropium for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Spain
Abstract
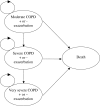
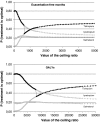
Our objective was to assess the 5-year cost effectiveness of bronchodilator therapy with tiotropium, salmeterol or ipratropium for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) from the perspective of the Spanish National Health System (NHS). A probabilistic Markov model was designed wherein patients moved between moderate, severe or very severe COPD and had the risk of exacerbation and death. Probabilities were derived from clinical trials. Spanish healthcare utilisation, costs and utilities were estimated for each COPD and exacerbation state. Outcomes were exacerbations, exacerbation-free months, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and cost(-effectiveness). The mean (SE) 5-year number of exacerbations was 3.50 (0.14) for tiotropium, 4.16 (0.40) for salmeterol and 4.71 (0.54) for ipratropium. The mean (SE) number of QALYs was 3.15 (0.08), 3.02 (0.15) and 3.00 (0.20), respectively. Mean (SE) 5-year costs were 6,424 euro (305 euro) for tiotropium, 5,869 euro (505 euro) for salmeterol, and 5,181 euro (682 euro) for ipratropium (2005 values). Ipratropium and tiotropium formed the cost-effectiveness frontier, with tiotropium being preferred when willingness to pay (WTP) exceeded 639 euro per exacerbation-free month and 8,157 euro per QALY. In Spain, tiotropium demonstrated the highest expected net benefit for ratios of the willingness to pay per QALY, well within accepted limits.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/thorax.58.9.803', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/thorax.58.9.803'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1746809', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1746809/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12947145', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12947145/'}]}
- Barnes, P.J.: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: new treatments for COPD. Thorax 58(9), 803–808 (2003) - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1053/rmed.2003.1441', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1053/rmed.2003.1441'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12645827', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12645827/'}]}
- Ayres, J.G., Price, M.J., Efthimiou, J.: Cost-effectiveness of fluticasone propionate in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a double-blind randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Respir. Med. 97(3), 212–220 (2003) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1053/rmed.2002.1293', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1053/rmed.2002.1293'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12117042', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12117042/'}]}
- Gallefoss, F., Bakke, P.S.: Cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness analysis of self-management in patients with COPD—a 1-year follow-up randomized, controlled trial. Respir. Med. 96(6), 424–431 (2002) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0149-2918(03)90039-7', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-2918(03)90039-7'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12637127', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12637127/'}]}
- Hogan, T.J., Geddes, R., Gonzalez, E.R.: An economic assessment of inhaled formoterol dry powder versus ipratropium bromide pressurized metered dose inhaler in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin. Ther. 25(1), 285–297 (2003) - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1053/rmed.2002.1425', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1053/rmed.2002.1425'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12556006', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12556006/'}]}
- Jones, P.W., Wilson, K., Sondhi, S.: Cost-effectiveness of salmeterol in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an economic evaluation. Respir. Med. 97(1), 20–26 (2003) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

