Distinct cytokine-driven responses of activated blood gammadelta T cells: insights into unconventional T cell pleiotropy
- PMID: 17371987
- PMCID: PMC3915340
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4304
Distinct cytokine-driven responses of activated blood gammadelta T cells: insights into unconventional T cell pleiotropy
Abstract
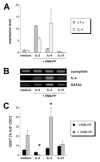
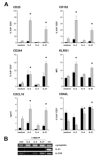
Human Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cells comprise a small population of peripheral blood T cells that in many infectious diseases respond to the microbial metabolite, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP), expanding to up to 50% of CD3(+) cells. This "transitional response," occurring temporally between the rapid innate and slower adaptive response, is widely viewed as proinflammatory and/or cytolytic. However, increasing evidence that different cytokines drive widely different effector functions in alphabeta T cells provoked us to apply cDNA microarrays to explore the potential pleiotropy of HMB-PP-activated Vgamma9/Vdelta2 T cells. The data and accompanying validations show that the related cytokines, IL-2, IL-4, or IL-21, each drive proliferation and comparable CD69 up-regulation but induce distinct effector responses that differ from prototypic alphabeta T cell responses. For example, the Th1-like response to IL-2 also includes expression of IL-5 and IL-13 that conversely are not induced by IL-4. The data identify specific molecules that may mediate gammadelta T cell effects. Thus, IL-21 induces a lymphoid-homing phenotype and high, unexpected expression of the follicular B cell-attracting chemokine CXCL13/BCA-1, suggesting a novel follicular B-helper-like T cell that may play a hitherto underappreciated role in humoral immunity early in infection. Such broad plasticity emphasizes the capacity of gammadelta T cells to influence the nature of the immune response to different challenges and has implications for the ongoing clinical application of cytokines together with Vgamma9/Vdelta2 TCR agonists.
Figures
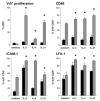
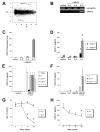
 ) of HMB-PP, together with the cytokines indicated, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell proliferation was assessed by expansion of Vγ9+CD3+ cells within the CD3+ lymphocyte population (n = 12). Expression of CD69 on Vγ9+ CD3+ cells was determined after 18 h (n = 8), expression of ICAM-1 (n = 6), and LFA-1 (n = 4) after 6 days.
) of HMB-PP, together with the cytokines indicated, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell proliferation was assessed by expansion of Vγ9+CD3+ cells within the CD3+ lymphocyte population (n = 12). Expression of CD69 on Vγ9+ CD3+ cells was determined after 18 h (n = 8), expression of ICAM-1 (n = 6), and LFA-1 (n = 4) after 6 days.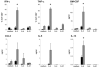
References
-
- Stockinger B, Bourgeois C, Kassiotis G. CD4+ memory T cells: functional differentiation and homeostasis. Immunol. Rev. 2006;211:39–48. - PubMed
-
- Vinuesa CG, Tangye SG, Moser B, Mackay CR. Follicular B helper T cells in antibody responses and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005;5:853–865. - PubMed
-
- Pennington DJ, Vermijlen D, Wise EL, Clarke SL, Tigelaar RE, Hayday AC. The integration of conventional and unconventional T cells that characterizes cell-mediated responses. Adv. Immunol. 2005;87:27–59. - PubMed
-
- Hayday AC. γδ cells: a right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000;18:975–1026. - PubMed
-
- Shires J, Theodoridis E, Hayday AC. Biological insights into TCRγδ+ and TCRαβ+ intraepithelial lymphocytes provided by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) Immunity. 2001;15:419–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

