IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability
- PMID: 17372023
- PMCID: PMC3724221
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4641
IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability
Abstract
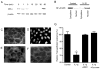
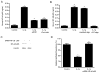
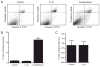
IL-1beta is a prototypical proinflammatory cytokine that plays a central role in the intestinal inflammation amplification cascade. Recent studies have indicated that a TNF-alpha- and IFN-gamma-induced increase in intestinal epithelial paracellular permeability may be an important mechanism contributing to intestinal inflammation. Despite its central role in promoting intestinal inflammation, the role of IL-1beta on intestinal epithelial tight junction (TJ) barrier function remains unclear. The major aims of this study were to determine the effect of IL-1beta on intestinal epithelial TJ permeability and to elucidate the mechanisms involved in this process, using a well-established in vitro intestinal epithelial model system consisting of filter-grown Caco-2 intestinal epithelial monolayers. IL-1beta (0-100 ng/ml) produced a concentration- and time-dependent decrease in Caco-2 transepithelial resistance. Conversely, IL-1beta caused a progressive time-dependent increase in transepithelial permeability to paracellular marker inulin. IL-1beta-induced increase in Caco-2 TJ permeability was accompanied by a rapid activation of NF-kappaB. NF-kappaB inhibitors, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate and curcumin, prevented the IL-1beta-induced increase in Caco-2 TJ permeability. To further confirm the role of NF-kappaB in the IL-1beta-induced increase in Caco-2 TJ permeability, NF-kappaB p65 expression was silenced by small interfering RNA transfection. NF-kappaB p65 depletion completely inhibited the IL-1beta-induced increase in Caco-2 TJ permeability. IL-1beta did not induce apoptosis in the Caco-2 cell. In conclusion, our findings show for the first time that IL-1beta at physiologically relevant concentrations causes an increase in intestinal epithelial TJ permeability. The IL-1beta-induced increase in Caco-2 TJ permeability was mediated in part by the activation of NF-kappaB pathways but not apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
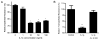
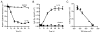


References
-
- Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–2147. - PubMed
-
- Casini-Raggi V, Kam L, Chong YJ, Fiocchi C, Pizarro TT, Cominelli F. Mucosal imbalance of IL-1 and IL-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease: a novel mechanism of chronic intestinal inflammation. J Immunol. 1995;154:2434–2440. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs KL, Sartor RB, Haskill S. Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:1587–1595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

