Determination of synephrine in bitter orange raw materials, extracts, and dietary supplements by liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection: single-laboratory validation
- PMID: 17373438
- PMCID: PMC3207213
Determination of synephrine in bitter orange raw materials, extracts, and dietary supplements by liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection: single-laboratory validation
Abstract
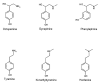
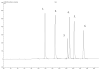
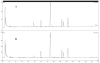
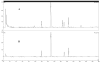
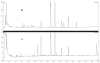
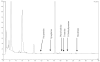
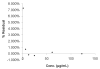
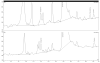
A method has been developed to quantify synephrine in bitter orange raw material, extracts, and dietary supplements. Single-laboratory validation has been performed on the method to determine the repeatability, accuracy, selectivity, limit of detection/limit of quantification (LOQ), ruggedness, and linearity for p-synephrine and 5 other biogenic amines: octopamine, phenylephrine (m-synephrine), tyramine, N-methyltyramine, and hordenine, which may be present in bitter orange. p-Synephrine was found to be the primary biogenic amine present in all materials tested, accounting for >80% of the total biogenic amine content in all samples except a finished product. Repeatability precision for synephrine was between 1.48 and 3.55% RSD. Synephrine recovery was between 97.5 and 104%. The minor alkaloids were typically near the LOQ of the method (300-900 microg/g) in the test materials, and between-day precision for the minor compounds was poor because interferences could sometimes be mistakenly identified as one of the minor analytes. Recoveries of the minor components ranged from 99.1 to 103% at approximately 6000 microg/g spike level, to 90.7 to 120% at 300 microg/g spike level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of Bitter Orange alkaloids in dietary supplements standard reference materials by liquid chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance and fluorescence detection.J Chromatogr A. 2007 Jul 13;1156(1-2):304-11. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.12.027. Epub 2007 May 23. J Chromatogr A. 2007. PMID: 17524413
-
Mass spectrometric determination of the predominant adrenergic protoalkaloids in bitter orange (Citrus aurantium).J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Nov 28;55(24):9769-75. doi: 10.1021/jf072030s. Epub 2007 Oct 30. J Agric Food Chem. 2007. PMID: 17966980
-
Analysis of bitter orange dietary supplements for natural and synthetic phenethylamines by LC-MS/MS.Drug Test Anal. 2020 Sep;12(9):1241-1251. doi: 10.1002/dta.2871. Epub 2020 Jun 28. Drug Test Anal. 2020. PMID: 32497396
-
[Synephrine in dietary supplements and specialized foodstuffs: biological activity, safety and methods of analysis].Vopr Pitan. 2021;90(6):101-113. doi: 10.33029/0042-8833-2021-90-6-101-113. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Vopr Pitan. 2021. PMID: 35032130 Review. Russian.
-
Chromatographic and electrophoretic methods for the analysis of phenethylamine [corrected] alkaloids in Citrus aurantium.J Chromatogr A. 2007 Aug 17;1161(1-2):71-88. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.097. Epub 2007 Jun 7. J Chromatogr A. 2007. PMID: 17582424 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical defense responses of upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. to physical wounding.Plant Direct. 2019 May 17;3(5):e00141. doi: 10.1002/pld3.141. eCollection 2019 May. Plant Direct. 2019. PMID: 31245779 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of p-synephrine alone and in combination with selected bioflavonoids on resting metabolism, blood pressure, heart rate and self-reported mood changes.Int J Med Sci. 2011 Apr 28;8(4):295-301. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8.295. Int J Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21537493 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the receptor-binding properties of p-synephrine as related to its pharmacological effects.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2011;2011:482973. doi: 10.1155/2011/482973. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2011. PMID: 21904645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p-Synephrine Indicates Internal Maturity of Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck cv. Mato Peiyu-Reclaiming Functional Constituents from Nonedible Parts.Molecules. 2023 May 22;28(10):4244. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104244. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241982 Free PMC article.
-
p-Synephrine, ephedrine, p-octopamine and m-synephrine: Comparative mechanistic, physiological and pharmacological properties.Phytother Res. 2020 Aug;34(8):1838-1846. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6649. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32101364 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ou M. Chinese-English Manual of Commonly Used Prescriptions in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Joint Publishing Co.; Hong Kong: 1989.
-
- Nagy S, Shaw PE, Veidhais MK. Citrus Science and Technology. Vol. 1. The AVI Publishing Co.; Bridgeport, CT: 1977.
-
- He X, Lian L, Lin L, Bernart MW. J. Chromatogr. A. 1997;791:127–134.
-
- Hashimoto K, Yasuda T, Ohsawa K. J. Chromatogr. 1992;623:386–389.
-
- Kusu F, Li X, Takamura K. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992;40:3284–3286.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
