The 5-HT3 receptor as a therapeutic target
- PMID: 17373882
- PMCID: PMC1994432
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.11.4.527
The 5-HT3 receptor as a therapeutic target
Abstract
The 5-HT3 receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. It is a member of the Cys-loop family of receptors, which also includes nicotinic acetylcholine, glycine and GABAA receptors. Each member of the family consists of an arrangement of five subunits surrounding a central ion-conducting pore. The 5-HT3 receptor binding site is composed of six loops from two adjacent subunits, and the critical ligand binding residues within these loops are well documented. There are a range of 5-HT3 receptor agonists and competitive antagonists, but it is the antagonists that dominate their clinical use. Studies have proposed a range of disease symptoms that might be amenable to 5-HT3 receptor selective compounds; however, so far only the treatment of emesis and irritable bowel syndrome have been fully realised. In this review, the authors look at the structure, function and distribution of 5-HT3 receptors and how this may influence their role in disease. The authors also describe the existing clinical applications of 5-HT3 antagonists and the future potential of these drugs.
Figures

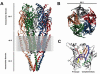

References
-
- DERKACH V, SURPRENANT A, NORTH RA. 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature. 1989;339(6227):706–709. - PubMed
-
- MARICQ AV, PETERSON AS, BRAKE AJ, MYERS RM, JULIUS D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991;254(5030):432–437. • First cloned 5-HT3 receptor subunit. - PubMed
-
- MIYAKE A, MOCHIZUKI S, TAKEMOTO Y, AKUZAWA S. Molecular cloning of human 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor: heterogeneity in distribution and function among species. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995;48(3):407–416. - PubMed
-
- FIEBICH BL, AKUNDI RS, SEIDEL M, et al. Expression of 5-HT3A receptors in cells of the immune system. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2004;33(Suppl. 119):9–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
