Baclofen blocks expression and sensitization of anxiety-like behavior in an animal model of repeated stress and ethanol withdrawal
- PMID: 17374037
- PMCID: PMC2864137
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00342.x
Baclofen blocks expression and sensitization of anxiety-like behavior in an animal model of repeated stress and ethanol withdrawal
Abstract
Background: Repeated exposures to forced ethanol diets (EDs) or restraint stress sensitize anxiety-like behavior during a future ethanol withdrawal. The present investigation assessed whether pretreatment of rats with agents targeting receptor systems thought to be important in treating relapse in alcoholic patients would prevent sensitization of anxiety-like behavior.
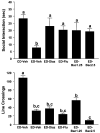
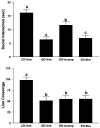
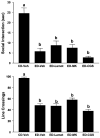
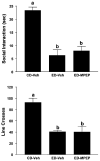
Methods: Groups of rats were exposed to either (1) three 5-day cycles of ED with 2 days of withdrawal between cycles, (2) continuous ED, or (3) 5 days of ED in a single cycle preceded by 2 episodes of restraint stress 6 days apart. Drugs [baclofen, acamprosate, naloxone, lamotrigine, ifenprodil, dizocilpine (MK-801), CGS19755, diazepam, flumazenil, or 6-methyl-2-(phenylethynyl)pyridine] were given prophylactically during the first and second withdrawal periods only or, in separate baclofen experiments, acutely during the third withdrawal or during withdrawal from continuous ED. Baclofen administration preceded each stress session in the stress-withdrawal protocols. Anxiety-like behavior was assessed in the social interaction (SI) test 5 hours after the ethanol was removed or after 3 days of abstinence.
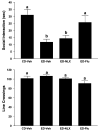
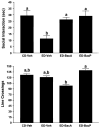
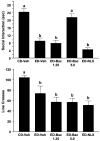
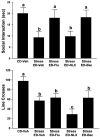
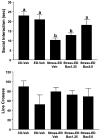
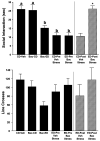
Results: Baclofen (1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg), flumazenil (5 mg/kg), and diazepam (1 mg/kg) blocked the reduction in SI induced by ethanol withdrawal. Among the drugs that alter glutamate function, only acamprosate (300 mg/kg) was effective. In the stress protocols, baclofen (5 mg/kg) given before each of the 2 restraint stress sessions before ethanol exposure or before stress during abstinence also attenuated SI deficits.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that GABAB and GABAA, but not glutamate or opioid mechanisms, are involved in adaptive changes associated with anxiety-like behavior induced by these repeated ethanol-withdrawal and stress-withdrawal paradigms. The lack of action of agents attenuating different aspects of glutamate function suggests that acamprosate's action is related to some other, as yet undetermined, mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior during later withdrawals by treatment of early withdrawals with benzodiazepine/gamma-aminobutyric acid ligands.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Apr;29(4):553-63. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000158840.07475.97. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 15834220 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization, duration, and pharmacological blockade of anxiety-like behavior following repeated ethanol withdrawal in adolescent and adult rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Mar;33(3):455-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00856.x. Epub 2008 Dec 13. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009. PMID: 19120055 Free PMC article.
-
Prior multiple ethanol withdrawals enhance stress-induced anxiety-like behavior: inhibition by CRF1- and benzodiazepine-receptor antagonists and a 5-HT1a-receptor agonist.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005 Sep;30(9):1662-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300706. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005. PMID: 15726114 Free PMC article.
-
Role of GABA(B) receptor in alcohol dependence: reducing effect of baclofen on alcohol intake and alcohol motivational properties in rats and amelioration of alcohol withdrawal syndrome and alcohol craving in human alcoholics.Neurotox Res. 2004;6(5):403-14. doi: 10.1007/BF03033315. Neurotox Res. 2004. PMID: 15545024 Review.
-
Alcohol withdrawal and conditioning.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Mar;29(3):453-64. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000156737.56425.e3. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 15770122 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of baclofen for alcohol dependence: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Nov;34(11):1849-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01273.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 20662805 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Baclofen and naltrexone effects on alcohol self-administration: Comparison of treatment initiated during abstinence or ongoing alcohol access in baboons.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017 Oct 1;179:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.06.019. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017. PMID: 28753481 Free PMC article.
-
Novel therapeutic strategies for alcohol and drug addiction: focus on GABA, ion channels and transcranial magnetic stimulation.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Jan;37(1):163-77. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.216. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22030714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of topiramate and other anti-glutamatergic drugs on the acute intoxicating actions of ethanol in mice: modulation by genetic strain and stress.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 May;34(6):1454-66. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.182. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18843265 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific microinjection of baclofen into the anterior ventral tegmental area reduces binge-like ethanol intake in male C57BL/6J mice.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Jun;123(3):555-63. doi: 10.1037/a0015345. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19485562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addolorato G, Caputo F, Capristo E, Colombo G, Gessa GL, Gasbarrini G. Ability of baclofen in reducing alcohol craving and intake: II—Preliminary clinical evidence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Addolorato G, Caputo E, Capristo E, Domenicali M, Bernardi M, Janin L, Agabio A, Colombo G, Gessa GL, Gasbarrini G. Baclofen efficacy in reducing alcohol craving and intake: a preliminary double-blind, randomized controlled study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002;37:504–508. - PubMed
-
- Addolorato G, Leggio L, Abenavoli L, Agabio R, Caputo F, Capristo E, Colombo G, Gessa GL, Gasbarrini G. Baclofen in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome: a comparative study vs diazepam. Am J Med. 2006;119:276.e13–18. - PubMed
-
- Akhondzadeh S, Ahmadi-Abhari SA, Assadi SM, Shabestari OL, Kashani AR, Farzanehgan ZM. Double-blind randomized controlled trial of baclofen vs. clonidine in the treatment of opiate withdrawal. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2000;25:347–353. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez C, Prunell M, Boada J. Effect of naloxone on behavioral changes induced by subchronic administration of ethanol in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998;59:961–965. - PubMed

