Obesity and the risk of gallbladder cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 17375043
- PMCID: PMC2360167
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603703
Obesity and the risk of gallbladder cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
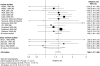
We performed a meta-analysis of studies of the association between excess body weight and risk of gallbladder cancer identified from MEDLINE and EMBASE databases from 1966 to February 2007 and the references of retrieved articles. A random-effects model was used to combine results from eight cohort studies and three case-control studies, with a total of 3288 cases. Compared with individuals of 'normal weight', the summary relative risk of gallbladder cancer for those who were overweight or obese was 1.15 (95% CI, 1.01-1.30) and 1.66 (95% CI, 1.47-1.88) respectively. The association with obesity was stronger for women (relative risk, 1.88; 95% CI, 1.66-2.13) than for men (relative risk, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.09-1.68). There was no statistically significant heterogeneity among the results of individual studies. This meta-analysis confirms the association between excess body weight and risk of gallbladder cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ (2003) Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med 348: 1625–1638 - PubMed
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7: 177–188 - PubMed
-
- Engeland A, Tretli S, Austad G, Bjørge T (2005) Height and body mass index in relation to colorectal and gallbladder cancer in two million Norwegian men and women. Cancer Causes Control 16: 987–996 - PubMed
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21: 1539–1558 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical