Oral administration of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb-761 inhibits thermal hyperalgesia in rodent models of inflammatory and post-surgical pain
- PMID: 17375081
- PMCID: PMC2013958
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707220
Oral administration of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb-761 inhibits thermal hyperalgesia in rodent models of inflammatory and post-surgical pain
Abstract
Background and purpose: Studies in vitro suggest that the standardised extract of Ginkgo biloba, EGb-761 has anti-inflammatory properties and modulatory effects on key pain-related molecules. This study investigated the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of EGb-761 on carrageenan-induced inflammatory and hindpaw incisional pain.
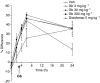
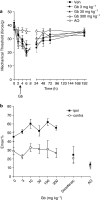
Experimental approach: Adult male Wistar rats (n=6-10/group; 250-420 g) were injected intradermally with carrageenan into the left hindpaw or anaesthetised with isoflurane (2%) and a longitudinal 1 cm incision was made through the skin, fascia and plantaris muscle of the hindpaw. EGb-761 (3, 10, 30, 100 or 300 mg kg(-1)), diclofenac (5 mg kg(-1)) or drug-vehicle was administered 3 h post-carrageenan/post-surgery. Hindpaw withdrawal latency (in seconds) to thermal stimulation, response threshold (in grams) to mechanical stimulation and paw volume were measured.
Key results: Carrageenan induced significant mechanical allodynia, thermal hyperalgesia and paw oedema at 6 h post-carrageenan, while paw incision surgery induced significant mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia at 6 and 24 h post-surgery. Administration of EGb-761 dose-dependently inhibited thermal hyperalgesia and was equally effective as diclofenac (5 mg kg(-1)) in both the carrageenan and hindpaw incision model. EGb-761 had no effect on carrageenan- or incision-induced mechanical allodynia or paw oedema. Diclofenac significantly reduced mechanical allodynia in both models and carrageenan-induced paw oedema.
Conclusions and implications: EGb-761 dose-dependently alleviates acute inflammatory and surgically induced thermal hyperalgesia and is comparable to diclofenac, a commonly prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. This indicates that EGb-761 has analgesic potential in acute inflammatory pain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Central and local administration of Gingko biloba extract EGb 761® inhibits thermal hyperalgesia and inflammation in the rat carrageenan model.Anesth Analg. 2011 May;112(5):1226-31. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182117440. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21474665
-
Bilobalide, a unique constituent of Ginkgo biloba, inhibits inflammatory pain in rats.Behav Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;24(4):298-306. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e32836360ab. Behav Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23838965 Clinical Trial.
-
Quantitative characterization of a repeated acute joint inflammation model in rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 May-Jun;34(5-6):520-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04606.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17439426
-
[Effect of local anesthetics on the postoperative inflammatory response].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2009 Mar;28(3):231-7. doi: 10.1016/j.annfar.2008.12.021. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2009. PMID: 19297121 Review. French.
-
Experimental animal models of muscle pain and analgesia.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2003 Oct;31(4):188-94. doi: 10.1097/00003677-200310000-00006. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2003. PMID: 14571958 Review.
Cited by
-
Enrichment and Purification of Total Ginkgo Flavonoid O-Glycosides from Ginkgo Biloba Extract with Macroporous Resin and Evaluation of Anti-Inflammation Activities In Vitro.Molecules. 2018 May 13;23(5):1167. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051167. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29757247 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of curcumin and Ginkgo biloba on matrix metalloproteinases gene expression and other biomarkers of inflammatory bowel disease.J Physiol Biochem. 2012 Dec;68(4):529-39. doi: 10.1007/s13105-012-0168-9. Epub 2012 Apr 26. J Physiol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22535283
-
Ginkgo biloba delays light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jun;21(6):576. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10008. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33850548 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone attenuates paw incision-induced spontaneous and evoked pain through anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory mechanisms in rats.Vet Res Forum. 2025;16(2):89-96. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2025053.4204. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Vet Res Forum. 2025. PMID: 40099240 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb761 Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Experimental Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice by Regulating the Balance of M1/M2 Macrophages and Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB)-Mediated Cellular Apoptosis.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Aug 16;26:e922634. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922634. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32799214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Salam ME, Baiumy AR, El-Batran S, Arbid SM. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive and gastric effects of Ginkgo Biloba in the rat. Pharmacol Res. 2004;49:133–142. - PubMed
-
- Anjaneyulu M, Chopra K. Quercetin, a biflavonoid, attenuates thermal hyperalgesia in a mouse model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2003;27:1001–1005. - PubMed
-
- Biber A, Koch E. Bioavailability of ginkgolides and bilobalide from extracts of ginkgo biloba using GC/MS. Planta Med. 1999;65:192–193. - PubMed
-
- Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain. 1996;64:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Curtis-Prior P, Vere D, Fray P. Therapeutic value of Ginkgo biloba in reducing symptoms of decline in mental function. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999;1:535–541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

