F15063, a compound with D2/D3 antagonist, 5-HT 1A agonist and D4 partial agonist properties. II. Activity in models of positive symptoms of schizophrenia
- PMID: 17375086
- PMCID: PMC2013947
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707159
F15063, a compound with D2/D3 antagonist, 5-HT 1A agonist and D4 partial agonist properties. II. Activity in models of positive symptoms of schizophrenia
Abstract
Background and purpose: F15063 is a high affinity D(2)/D(3) antagonist, D(4) partial agonist, and high efficacy 5-HT(1A) agonist, with little affinity (40-fold lower than for D(2) receptors) at other central targets. Here, the profile of F15063 was evaluated in models of positive symptoms of schizophrenia and motor side-effects.
Experimental approach: Rodent behavioural tests were based on reversal of hyperactivity induced by psychostimulants and on measures of induction of catalepsy and 'serotonin syndrome'.
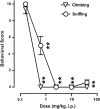
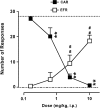
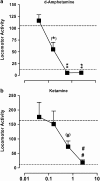
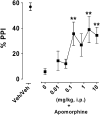
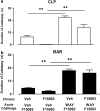
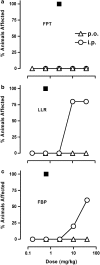
Key results: F15063 potently (ED(50)s: 0.23 to 1.10 mg kg(-1) i.p.) reversed methylphenidate-induced stereotyped behaviors, blocked d-amphetamine and ketamine hyperlocomotion, attenuated apomorphine-induced prepulse inhibition (PPI) deficits, and was active in the conditioned avoidance test. In mice, it reversed apomorphine-induced climbing (ED(50)=0.30 mg kg(-1) i.p.). F15063, owing to its 5-HT(1A) agonism, did not produce (ED(50)>40 mg kg(-1) i.p.) catalepsy in rats and mice, a behavior predictive of occurrence of extra-pyramidal syndrome (EPS) in man. This absence of cataleptogenic activity was maintained upon sub-chronic treatment of rats for 5 days at 40 mg kg(-1) p.o. Furthermore, F15063 did not induce the 'serotonin syndrome' in rats (flat body posture and forepaw treading: ED(50) >32 mg kg(-1) i.p.).
Conclusions and implications: F15063 conformed to the profile of an atypical antipsychotic, with potent actions in models of hyperdopaminergic activity but without inducing catalepsy. These data suggest that F15063 may display potent antipsychotic actions with low EPS liability. This profile is complemented by a favourable profile in rodent models of negative symptoms and cognitive deficits of schizophrenia (companion paper).
Figures
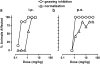
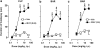
Comment in
-
Optimisation of anti-psychotic therapeutics: a balancing act?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 May;151(2):161-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707164. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17375084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assie MB, Bardin L, Auclair A, Consul-Denjean N, Sautel F, Kleven MS, et al. F15063, a novel antipsychotic with dopamine D2/D3 antagonist, 5-HT1A agonist and D4 partial agonist properties: III) Duration of brain D2-like receptor occupancy, antipsychotic-like activity and plasma concentration in rodents Neuropsychopharmacology 200616Suppl 45432P3D007
-
- Auclair A, Kleven MS, Besnard J, Depoortère R, Newman-Tancredi A. Actions of novel antipsychotic agents on apomorphine-induced PPI disruption: influence of combined serotonin 5-HT1A receptor activation and dopamine D2 receptor blockade. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006a;31:1900–1909. - PubMed
-
- Auclair A, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortère R. Comparative analysis of typical, atypical, and novel antipsychotics with preferential D2/D3 and 5-HT1A affinity in rodent models of cognitive flexibility and sensory gating: (II) The reversal learning task and PPI of the startle reflex. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006b;9 Suppl 1:P01.167.
-
- Bantick RA, Deakin JF, Grasby PM. The 5-HT1A receptor in schizophrenia: a promising target for novel atypical neuroleptics. J Psychopharmacol. 2001;15:37–46. - PubMed
-
- Bardin L, Auclair A, Kleven MS, Prinssen EPM, Koek W, Newman-Tancredi A, et al. Pharmacological profiles in rats of novel antipsychotics with combined dopamine D2/serotonin 5-HT1a activity: comparison with typical and atypical conventional antipsychotics Behav Pharmacol(in press) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

