A key role of dendritic cells in probiotic functionality
- PMID: 17375199
- PMCID: PMC1819555
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000313
A key role of dendritic cells in probiotic functionality
Abstract
Background: Disruption of the intestinal homeostasis and tolerance towards the resident microbiota is a major mechanism involved in the development of inflammatory bowel disease. While some bacteria are inducers of disease, others, known as probiotics, are able to reduce inflammation. Because dendritic cells (DCs) play a central role in regulating immune responses and in inducing tolerance, we investigated their role in the anti-inflammatory potential of probiotic lactic acid bacteria.
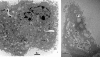
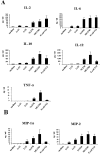
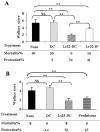
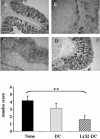
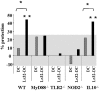
Methodology/principal findings: Selected LAB strains, while efficiently taken up by DCs in vitro, induced a partial maturation of the cells. Transfer of probiotic-treated DCs conferred protection against 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. Protection was associated with a reduction of inflammatory scores and colonic expression of pro-inflammatory genes, while a high local expression of the immunoregulatory enzyme indolamine 2, 3 dioxgenase (IDO) was observed. The preventive effect of probiotic-pulsed DCs required not only MyD88-, TLR2- and NOD2-dependent signaling but also the induction of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory cells in an IL-10-independent pathway.
Conclusions/significance: Altogether, these results suggest that selected probiotics can stimulate DC regulatory functions by targeting specific pattern-recognition receptors and pathways. The results not only emphasize the role of DCs in probiotic immune interactions, but indicate a possible role in immune-intervention therapy for IBD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory capacity of selected lactobacilli in experimental colitis is driven by NOD2-mediated recognition of a specific peptidoglycan-derived muropeptide.Gut. 2011 Aug;60(8):1050-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.232918. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Gut. 2011. PMID: 21471573
-
Generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells using Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii as tolerogenic probiotics.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Sep;119(9):7865-7872. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27203. Epub 2018 Jun 26. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29943843
-
Live and heat-killed probiotic Lactobacillus casei Lbs2 protects from experimental colitis through Toll-like receptor 2-dependent induction of T-regulatory response.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jul;36:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.03.033. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27107798
-
Intestinal dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep 7;17(33):3761-75. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3761. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic-Induced Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells: A Novel Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 31;22(15):8274. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158274. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Host interactions of probiotic bacterial surface molecules: comparison with commensals and pathogens.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Mar;8(3):171-84. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2297. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20157338 Review.
-
99th Dahlem conference on infection, inflammation and chronic inflammatory disorders: induction and control of regulatory T cells in the gastrointestinal tract: consequences for local and peripheral immune responses.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Apr;160(1):35-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04131.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20415849 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Influenced by Postbiotics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 15;22(24):13475. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413475. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes and molecules of lactobacilli supporting probiotic action.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008 Dec;72(4):728-64, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00017-08. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19052326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supernatant from bifidobacterium differentially modulates transduction signaling pathways for biological functions of human dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2008 Jul 23;3(7):e2753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002753. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18648505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Nussenzweig MC. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:685–711. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells: key controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 2000;101:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Duchmann R, Schmitt E, Knolle P, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Neurath M. Tolerance towards resident intestinal flora in mice is abrogated in experimental colitis and restored by treatment with interleukin-10 or antibodies to interleukin-12. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:934–938. - PubMed
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S, Medzhitov R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell. 2004;118:229–241. - PubMed
-
- Neish AS, Gewirtz AT, Zeng H, Young AN, Hobert ME, et al. Prokaryotic regulation of epithelial responses by inhibition of IkappaB-alpha ubiquitination. Science. 2000;289:1560–1563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

