Localization of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the articular surface of the rat femur
- PMID: 17375206
- PMCID: PMC1828076
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.06015
Localization of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the articular surface of the rat femur
Abstract
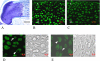
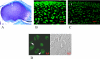
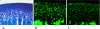
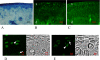
It has been suggested that the degradation of the articular cartilage and osteoarthritis (OA) are associated with gender and the estrogen hormone. Although many investigators have reported the presence of the estrogen receptors (ERs) alpha and beta in the articular cartilage, the localization of these receptors and the difference in their in vivo expression have not yet been clearly demonstrated. We performed immunofluorescence staining of ERalpha and ERbeta to elucidate the localization of the ERs and to note the effects of gender and the aging process on these receptors. The results revealed that ERalpha and ERbeta were expressed in the articular cartilage and subchondral bone layers of adult rats of both sexes. We also observed the high expression of these receptors in immature rats. In contrast, their expression levels decreased in an ovariectomised model, as a simulation of postmenopause, and in aged female rats. Therefore, this study suggests the direct effects of estrogen and ER expression on articular surface metabolism.
Figures



References
-
- Barrett-Connor E., Stuenkel C. A. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)—risks and benefits. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001;30:423–426. - PubMed
-
- Brandenberger A. W., Tee M. K., Lee J. Y., Chao V., Jaffe R. B. Tissue distribution of estrogen receptors alpha (ER-alpha) and beta (ER-beta) mRNA in the midgestational human fetus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997;82:3509–3512. - PubMed
-
- Creutz L. M., Kritzer M. F. Mesostriatal and mesolimbic projections of midbrain neurons immunoreactive for estrogen receptor beta or androgen receptors in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004;476:348–362. - PubMed
-
- Felson D. T., Nevitt M. C. Estrogen and osteoarthritis: how do we explain conflicting study results? Prev. Med. 1999;28:445–448. 449–450. discussion . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

