Induction of T-cell activation or anergy determined by the combination of intensity and duration of T-cell receptor stimulation, and sequential induction in an individual cell
- PMID: 17376194
- PMCID: PMC2265954
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02586.x
Induction of T-cell activation or anergy determined by the combination of intensity and duration of T-cell receptor stimulation, and sequential induction in an individual cell
Abstract
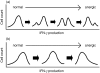
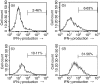
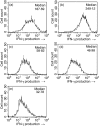
It has been shown that anergic T cells have important roles in peripheral tolerance, although the precise mechanism for inducing anergy is still unclear. We analysed the kinetics of anergy induction at an individual cell level by flow cytometry. We first successfully obtained T helper type 1 (Th1) cells that had been made uniform with the level of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production induced by antigen stimulation. We then used these Th1 cells to evaluate the degree of anergy for each Th1 cell treated with an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody according to the level of IFN-gamma secretion. Our results demonstrate that anergic stimulation could induce both activation and anergy, depending on the duration and intensity of stimulation at the level of an individual cell. Each Th1 cell was first activated and then gradually became anergic depending on the duration of stimulation. The duration of the stimulus required for inducing anergy became shorter as the intensity of stimulation became stronger. We also show that the calcineurin signal controlled the induction of activation or anergy depending on the activity. This study contributes to better understanding of the precise mechanism for inducing T-cell anergy.
Figures
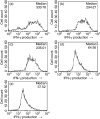
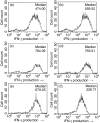
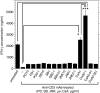
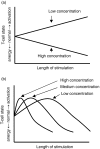
References
-
- Melamed D, Friedman A. Direct evidence for anergy in T lymphocytes tolerized by oral administration of ovalbumin. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:935–42. - PubMed
-
- Melamed D, Fishman-Lovell J, Uni Z, Weiner HL, Friedman A. Peripheral tolerance of Th2 lymphocytes induced by continuous feeding of ovalbumin. Int Immunol. 1996;8:717–24. - PubMed
-
- Salojin KV, Zhang J, Madrenas J, Delovitch TL. T-cell anergy and altered T-cell receptor signaling: effects on autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1998;19:468–73. - PubMed
-
- Whitacre CC, Gienapp IE, Orosz CG, Bitar DM. Oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. III. Evidence for clonal anergy. J Immunol. 1991;147:2155–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

