Variable influences of iodine on the T-cell recognition of a single thyroglobulin epitope
- PMID: 17376195
- PMCID: PMC2265959
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02584.x
Variable influences of iodine on the T-cell recognition of a single thyroglobulin epitope
Abstract
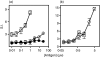
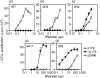
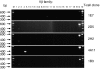
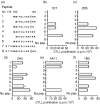
We have previously shown that iodotyrosyl formation within certain innocuous thyroglobulin (Tg) peptides confers on them immunopathogenic properties. In this report, we generated a panel of T-cell hybridoma clones specific for the immunogenic 16 mer Tg peptide p179 (amino acids 179-94) or its iodinated analogue (I-p179), with a view to examining the effects of a single iodine atom at the Y192 amino acid residue on T-cell recognition. We found that the peptide p179 was subdominant, and its binding to both A(k) and E(k) molecules was not significantly influenced by iodine. T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement was unaffected by the bulky iodine atom in two clones that responded to both analogues but it was sterically hindered in two other clones that recognized only p179. One clone was reactive only to I-p179, suggesting that the iodine atom is an integral part of its TCR ligand. Truncation analysis localized the determinant seen by all clones within the 11 mer peptide p184 (amino acids 184-194), suggesting that the cross-reactive clones were not activated by a minimal epitope lacking Y192 and that the negative influence of iodine was not the result of a flanking residue effect. These results demonstrate, at the clonal level, variable influences of a single iodine atom on the recognition of a single Tg peptide. Iodination of tyrosyl-containing, immunopathogenic Tg peptides may have unpredictable effects at the polyclonal level, depending on the extent of iodination at the particular site, and the relative number or effector function of autoreactive T-cell clones that are switched on or off by the neoantigenic determinant.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modifying effects of iodine on the immunogenicity of thyroglobulin peptides.J Autoimmun. 2007 Jun;28(4):171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Feb 26. J Autoimmun. 2007. PMID: 17327138
-
Unique role of thyroxine in T cell recognition of a pathogenic peptide in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis.Eur J Immunol. 1996 Apr;26(4):768-72. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260407. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8625966
-
Diverse fine specificity and receptor repertoire of T cells reactive to the major VP1 epitope (VP1230-250) of Theiler's virus: V beta restriction correlates with T cell recognition of the c-terminal residue.J Immunol. 1999 Jun 15;162(12):7049-57. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10358147
-
T-cell receptor-derived peptides in immunoregulation and therapy of retrovirally induced immunosuppression.Crit Rev Immunol. 2001;21(1-3):57-74. Crit Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11642614 Review.
-
The role of iodine in autoimmune thyroiditis.Crit Rev Immunol. 1997;17(5-6):511-7. Crit Rev Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9419438 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of HLA-DRB1∗03:01 and H2E transgenic mouse strains to correlate pathogenic thyroglobulin epitopes for autoimmune thyroiditis.J Autoimmun. 2011 Sep;37(2):63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.010. Epub 2011 Jun 17. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21683551 Free PMC article.
-
IL-9-Producing Th9 Cells Participate in the Occurrence and Development of Iodine-Induced Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Nov;201(11):5298-5308. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03598-z. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 36773201
-
Iodine, thyroid autoimmunity and cancer.Eur Thyroid J. 2015 Mar;4(1):26-35. doi: 10.1159/000371741. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Eur Thyroid J. 2015. PMID: 25960959 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine excess as an environmental risk factor for autoimmune thyroid disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 21;15(7):12895-912. doi: 10.3390/ijms150712895. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25050783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine epitope mapping within the pathogenic thyroglobulin peptide 2340-2359: minimal epitopes retaining antigenicity across various MHC haplotypes are not necessarily immunogenic.Immunology. 2012 Mar;135(3):245-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03538.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22098450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braverman LE, Ingbar SH, Vagenakis AG, Adams L, Maloof F. Enhanced susceptibility to iodide myxedema in patients with Hashimoto's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971;32:515–21. - PubMed
-
- Boyages SC, Bloot AM, Maberly GF, et al. Thyroid autoimmunity in endemic goitre caused by excessive iodine intake. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1989;31:453–65. - PubMed
-
- Robuschi G, Safran M, Braverman LE, Gnudi A, Roti E. Hypothyroidism in the elderly. Endocr Rev. 1987;8:142–53. - PubMed
-
- Tajiri J, Higashi K, Morita M, Umeda T, Sato T. Studies of hypothyroidism in patients with high iodine intake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986;63:412–17. - PubMed
-
- Kahaly GJ, Dienes HP, Beyer J, Hommel G. Iodide induces thyroid autoimmunity in patients with endemic goitre: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998;139:290–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

