Distinct signalling pathways promote phagocytosis of bacteria, latex beads and lipopolysaccharide in medfly haemocytes
- PMID: 17376199
- PMCID: PMC2265961
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02576.x
Distinct signalling pathways promote phagocytosis of bacteria, latex beads and lipopolysaccharide in medfly haemocytes
Abstract
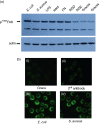
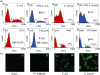
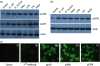
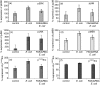
In insects, phagocytosis is an important innate immune response against pathogens and parasites, and several signal transduction pathways regulate this process. The focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/Src and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are of central importance because their activation upon pathogen challenge regulates phagocytosis via haemocyte secretion and activation of the prophenoloxidase (proPO) cascade. The goal of this study was to explore further the mechanisms underlying the process of phagocytosis. In particular, in this report, we used flow cytometry, RNA interference, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Western blot and immunoprecipitation analysis to demonstrate that (1) phagocytosis of bacteria (both Gram-negative and Gram-positive) is dependent on RGD-binding receptors, FAK/Src and MAPKs, (2) latex bead phagocytosis is RGD-binding-receptor-independent and dependent on FAK/Src and MAPKs, (3) lipopolysaccharide internalization is RGD-binding-receptor-independent and FAK/Src-independent but MAPK-dependent and (4) in unchallenged haemocytes in suspension, FAK, Src and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling molecules participating in phagocytosis show both a functional and a physical association. Overall, this study has furthered knowledge of FAK/Src and MAPK signalling pathways in insect haemocyte immunity and has demonstrated that distinct signalling pathways regulate the phagocytic activity of biotic and abiotic components in insect haemocytes. Evidently, the basic phagocytic signalling pathways among insects and mammals appear to have remained unchanged during evolution.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A beta integrin subunit regulates bacterial phagocytosis in medfly haemocytes.Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Jul;33(7):858-66. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2009.02.004. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19428487
-
Apoptosis in medfly hemocytes is regulated during pupariation through FAK, Src, ERK, PI-3K p85a, and Akt survival signaling.J Cell Biochem. 2007 May 15;101(2):331-47. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21175. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17177294
-
Uptake of LPS/E. coli/latex beads via distinct signalling pathways in medfly hemocytes: the role of MAP kinases activation and protein secretion.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 May 15;1744(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.031. Epub 2004 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15878392
-
Regulators and signalling in insect haemocyte immunity.Cell Signal. 2009 Feb;21(2):186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.08.014. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 18790716 Review.
-
Haemocyte-mediated immunity in insects: Cells, processes and associated components in the fight against pathogens and parasites.Immunology. 2021 Nov;164(3):401-432. doi: 10.1111/imm.13390. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 34233014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of genes isolated from plated hemocytes of the Pacific oyster, Crassostreas gigas.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2009 Jan-Feb;11(1):24-44. doi: 10.1007/s10126-008-9117-6. Epub 2008 Jul 12. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2009. PMID: 18622569
-
Intracellular HMGB1 negatively regulates efferocytosis.J Immunol. 2011 Nov 1;187(9):4686-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101500. Epub 2011 Sep 28. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21957148 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune properties of selected human neuropeptides against Moraxella catarrhalis and nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae.BMC Immunol. 2012 May 2;13:24. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-24. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22551165 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Hemocytes from Larvae of the Japanese Rhinoceros Beetle Allomyrina dichotoma (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and the Cellular Immune Response to Microorganisms.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 1;10(6):e0128519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128519. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26030396 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity in insects: surface-associated dopa decarboxylase-dependent pathways regulate phagocytosis, nodulation and melanization in medfly haemocytes.Immunology. 2008 Apr;123(4):528-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02722.x. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 17983437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamprou I, Tsakas SGL, Theodorou Karakantza M, Lampropoulou M, Marmaras VJ. Uptake of LPS/E. coli/latex beads via distinct signalling pathways in medfly. hemocytes: the role of MAP kinases activation and protein secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1744:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Mavrouli MD, Tsakas S, Theodorou GL, Lampropoulou M, Marmaras VJ. MAP kinases mediate phagocytosis and melanization via prophenoloxidase activation in medfly hemocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1744:145–56. - PubMed
-
- Soldatos AN, Metheniti A, Mamali I, Lambropoulou M, Marmaras VJ. Distinct LPS-induced signals regulate LPS uptake and morphological changes in medfly hemocytes. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;33:1075–84. - PubMed
-
- Metheniti A, Paraskevopoulou N, Lambropoulou M, Marmaras VJ. Involvement of FAK/Src complex in the processes of Escherichia coli phagocytosis by insect hemocytes. FEBS Lett. 2001;496:55–9. - PubMed
-
- Foukas LC, Katsoulas HL, Paraskevopoulou N, Metheniti A, Lambropoulou M, Marmaras VJ. Phagocytosis of Escherichia coli by insect hemocytes requires both activation of the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway for attachment and beta3 integrin for internalisation. J Biol Chem. 1998;24:14813–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

