Nanoconjugate based on polymalic acid for tumor targeting
- PMID: 17376417
- PMCID: PMC2329596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2007.01.015
Nanoconjugate based on polymalic acid for tumor targeting
Abstract
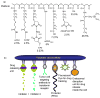
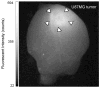
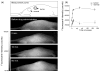
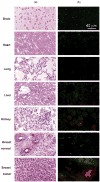
A new prototype of polymer-derived drug delivery system, the nanoconjugate Polycefin, was tested for its ability to accumulate in tumors based on enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect and receptor mediated endocytosis. Polycefin was synthesized for targeted delivery of Morpholino antisense oligonucleotides into certain tumors. It consists of units that are covalently conjugated with poly(beta-l-malic acid) (M(w) 50,000, M(w)/M(n) 1.3) highly purified from cultures of myxomycete Physarum polycephalum. The units are active in endosomal uptake, disruption of endosomal membranes, oligonucleotide release in the cytoplasm, and protection against enzymatic degradation in the vascular system. The polymer is biodegradable, non-immunogenic and non-toxic. Polycefin was also coupled with AlexaFluor 680 C2-maleimide dye for in vivo detection. Nude mice received subcutaneous injections of MDA-MB 468 human breast cancer cells into the left posterior mid-dorsum or intracranial injections of human glioma cell line U87MG. Polycefin at concentration of 2.5mg/kg was injected via the tail vein. In vivo fluorescence tumor imaging was performed at different time points, 0-180 min up to 24h after the drug injection. The custom-made macro-illumination imaging MISTI system was used to examine the in vivo drug accumulation in animals bearing human breast and brain tumors. In breast tumors the fluorescence signal in large blood vessels and in the tumor increased rapidly until 60 min and remained in the tumor at a level 6 times higher than in non-tumor tissue (180 min) (p<0.003). In brain tumors drug accumulated selectively in 24h without any detectable signal in non-tumor areas. The results of live imaging were corroborated histologically by fluorescence microscopic examination of various organs. In addition to tumors, only kidney and liver showed some fluorescent signal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polycefin, a new prototype of a multifunctional nanoconjugate based on poly(beta-L-malic acid) for drug delivery.Bioconjug Chem. 2006 Mar-Apr;17(2):317-26. doi: 10.1021/bc0502457. Bioconjug Chem. 2006. PMID: 16536461 Free PMC article.
-
Polymalic acid-based nanobiopolymer provides efficient systemic breast cancer treatment by inhibiting both HER2/neu receptor synthesis and activity.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 15;71(4):1454-64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3093. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21303974 Free PMC article.
-
Brain tumor tandem targeting using a combination of monoclonal antibodies attached to biopoly(beta-L-malic acid).J Control Release. 2007 Oct 8;122(3):356-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.05.032. Epub 2007 Jun 5. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17630012 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(malic acid) nanoconjugates containing various antibodies and oligonucleotides for multitargeting drug delivery.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2008 Apr;3(2):247-65. doi: 10.2217/17435889.3.2.247. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2008. PMID: 18373429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural and synthetic poly(malic acid)-based derivates: a family of versatile biopolymers for the design of drug nanocarriers.J Drug Target. 2014 Aug;22(7):556-75. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2014.936871. J Drug Target. 2014. PMID: 25012064 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Nanopolymers for Blood-Brain Barrier Delivery and Inhibition of Glioblastoma Growth through EGFR/EGFRvIII, c-Myc, and PD-1.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;11(11):2892. doi: 10.3390/nano11112892. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835657 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical Applications of Translational Optical Imaging: From Molecules to Humans.Molecules. 2021 Nov 2;26(21):6651. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216651. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(β-L-malic acid) production by diverse phylogenetic clades of Aureobasidium pullulans.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Jan;39(1):125-32. doi: 10.1007/s10295-011-1007-7. Epub 2011 Jul 2. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 21720775
-
Nanoconjugate Platforms Development Based in Poly(β,L-Malic Acid) Methyl Esters for Tumor Drug Delivery.J Nanotechnol. 2010;2010:825363. doi: 10.1155/2010/825363. J Nanotechnol. 2010. PMID: 23024655 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Two Types of Polymeric Micelles Based on Poly(β-L-Malic Acid) for Antitumor Drug Delivery.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0162607. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162607. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27649562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee BS, Vert M, Holler E. Water-soluble aliphatic polyesters; poly(malic acid)s. In: Doi Y, Steinbüchel A, editors. Biopolymers. 3a. Polyesters, Wiley–VCH; Weinheim: 2002. pp. 75–103.
-
- Ljubimova JY, Fugita M, Khazenzon NM, Das A, Pikul BB, Newman D, Sekiguchi K, Sorokin LM, Sasaki T, Black KL. Laminin-8 association with glial tumor grade, recurrence and patient survival. Cancer. 2004;101:604–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

