Function of the ATR N-terminal domain revealed by an ATM/ATR chimera
- PMID: 17376433
- PMCID: PMC1855264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.02.015
Function of the ATR N-terminal domain revealed by an ATM/ATR chimera
Abstract
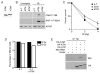
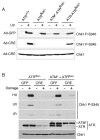
The ATM and ATR kinases function at the apex of checkpoint signaling pathways. These kinases share significant sequence similarity, phosphorylate many of the same substrates, and have overlapping roles in initiating cell cycle checkpoints. However, they sense DNA damage through distinct mechanisms. ATR primarily senses single stranded DNA (ssDNA) through its interaction with ATRIP, and ATM senses double strand breaks through its interaction with Nbs1. We determined that the N-terminus of ATR contains a domain that binds ATRIP. Attaching this domain to ATM allowed the fusion protein (ATM*) to bind ATRIP and associate with RPA-coated ssDNA. ATM* also gained the ability to localize efficiently to stalled replication forks as well as double strand breaks. Despite having normal kinase activity when tested in vitro and being phosphorylated on S1981 in vivo, ATM* is defective in checkpoint signaling and does not complement cellular deficiencies in either ATM or ATR. These data indicate that the N-terminus of ATR is sufficient to bind ATRIP and to promote localization to sites of replication stress.
Figures




References
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, Orntoft T, Lukas J, Bartek J. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;434:864–870. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Tort F, Fugger K, Johansson F, Sehested M, Andersen CL, Dyrskjot L, Orntoft T, Lukas J, Kittas C, Helleday T, Halazonetis TD, Bartek J, Gorgoulis VG. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444:633–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

