Organization of cytokeratin cytoskeleton and germ plasm in the vegetal cortex of Xenopus laevis oocytes depends on coding and non-coding RNAs: three-dimensional and ultrastructural analysis
- PMID: 17376434
- PMCID: PMC2613015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.02.018
Organization of cytokeratin cytoskeleton and germ plasm in the vegetal cortex of Xenopus laevis oocytes depends on coding and non-coding RNAs: three-dimensional and ultrastructural analysis
Abstract
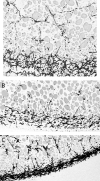
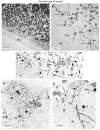
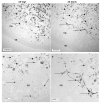
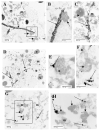
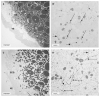
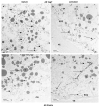
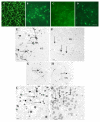
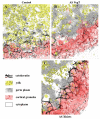
Recent studies discovered a novel structural role of RNA in maintaining the integrity of the mitotic spindle and cellular cytoskeleton. In Xenopus laevis, non-coding Xlsirts and coding VegT RNAs play a structural role in anchoring localized RNAs, maintaining the organization of the cytokeratin cytoskeleton and germinal granules in the oocyte vegetal cortex and in subsequent development of the germline in the embryo. We studied the ultrastructural effects of antisense oligonucleotide driven ablation of Xlsirts and VegT RNAs on the organization of the cytokeratin, germ plasm and other components of the vegetal cortex. We developed a novel method to immunolabel and visualize cytokeratin at the electron microscopy level, which allowed us to reconstruct the ultrastructural organization of the cytokeratin network relative to the components of the vegetal cortex in Xenopus oocytes. The removal of Xlsirts and VegT RNAs not only disrupts the cytokeratin cytoskeleton but also has a profound transcript-specific effect on the anchoring and distribution of germ plasm islands and their germinal granules and the arrangement of yolk platelets within the vegetal cortex. We suggest that the cytokeratin cytoskeleton plays a role in anchoring of germ plasm islands within the vegetal cortex and germinal granules within the germ plasm islands.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential structural role of non-coding and coding RNAs in the organization of the cytoskeleton at the vegetal cortex of Xenopus oocytes.Development. 2005 Aug;132(15):3445-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.01919. Epub 2005 Jul 6. Development. 2005. PMID: 16000384
-
Structural messenger RNA contains cytokeratin polymerization and depolymerization signals.Cell Tissue Res. 2011 Nov;346(2):209-22. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1255-x. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Cell Tissue Res. 2011. PMID: 21987223
-
Three-dimensional ultrastructural analysis of RNA distribution within germinal granules of Xenopus.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 1;241(1):79-93. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0488. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784096
-
Organisation of Xenopus oocyte and egg cortices.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Mar 15;44(6):415-29. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19990315)44:6<415::AID-JEMT3>3.0.CO;2-4. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10211675 Review.
-
RNA localization and germ cell determination in Xenopus.Int Rev Cytol. 2001;203:63-91. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(01)03004-2. Int Rev Cytol. 2001. PMID: 11131528 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal messages to live by: a personal historical perspective.Genesis. 2017 Jan;55(1-2):10.1002/dvg.23007. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23007. Genesis. 2017. PMID: 28095642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of antisense oligonucleotides in Xenopus oocytes.Methods. 2010 May;51(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.12.015. Epub 2010 Jan 5. Methods. 2010. PMID: 20045732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world.Genes Dev. 2009 Jul 1;23(13):1494-504. doi: 10.1101/gad.1800909. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19571179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the regulation of RNP granule assembly in oocytes.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;295:233-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394306-4.00013-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22449492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA granules in germ cells.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Dec 1;3(12):a002774. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002774. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21768607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bashirullah A, Cooperstock RL, Lipshitz HD. RNA localization in development. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:335–394. - PubMed
-
- Jansen RP. mRNA localization: message on the move. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001;2:247–256. - PubMed
-
- King ML, Zhou Y, Bubunenko M. Polarizing genetic information in the egg: RNA localization in the frog oocyte. BioEssays. 1999;21:546–557. - PubMed
-
- Kloc M, Zearfoss NR, Etkin LD. Mechanisms of subcellular mRNA localization. Cell. 2002b;108:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Palacios IM, Johnston D. Getting the message across: the intracellular localization of mRNA in higher eukaryotes. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2001;17:569–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

