Multilocus sequence typing of the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 17376886
- PMCID: PMC1865896
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00064-07
Multilocus sequence typing of the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
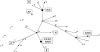
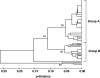
A multilocus sequence typing (MLST) scheme was devised for Aspergillus fumigatus. The system involved sequencing seven gene fragments and was applied to a panel of 100 isolates of A. fumigatus from diverse sources. Thirty different sequence types were found among the 100 isolates, and 93% of the isolates differed from the other isolates by only one allele sequence, forming a single clonal cluster as indicated by the eBURST algorithm. The discriminatory power of the MLST method was only 0.93. These results strongly indicate that A. fumigatus is a species of a relatively recent origin, with low levels of sequence dissimilarity. Typing methods based on variable numbers of tandem repeats offer higher levels of strain discrimination. Mating type data for the 100 isolates showed that 71 isolates were type MAT1-2 and 29 isolates were MAT1-1.
Figures
References
-
- Bart-Delabesse, E., J. Sarfati, J.-P. Debeaupuis, W. Van Leeuwen, A. Van Belkum, S. Bretagne, and J.-P. Latge. 2001. Comparison of restriction fragment length polymorphism, microsatellite length polymorphism, and random amplification of polymorphic DNA analyses for fingerprinting Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:2683-2686. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertout, S., F. Renaud, T. De Meeüs, M.-A. Piens, B. Lebeau, M.-A. Viviani, M. Mallié, J.-M. Bastide, and the EBGA Network. 2000. Multilocus enzyme electrophoresis analysis of Aspergillus fumigatus strains isolated from the first clinical sample from patients with invasive aspergillosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 49:375-381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

