The autoregulatory and transactivating functions of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein use independent mechanisms for promoter binding
- PMID: 17376893
- PMCID: PMC1900308
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02437-06
The autoregulatory and transactivating functions of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein use independent mechanisms for promoter binding
Abstract
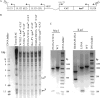
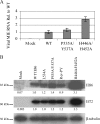
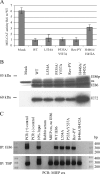
The functions of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) IE86 protein are paradoxical, as it can both activate and repress viral gene expression through interaction with the promoter region. Although the mechanism for these functions is not clearly defined, it appears that a combination of direct DNA binding and protein-protein interactions is involved. Multiple sequence alignment of several HCMV IE86 homologs reveals that the amino acids (534)LPIYE(538) are conserved between all primate and nonprimate CMVs. In the context of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), mutation of both P535 and Y537 to alanines (P535A/Y537A) results in a nonviable BAC. The defective HCMV BAC does not undergo DNA replication, although the P535A/Y537A mutant IE86 protein appears to be stably expressed. The P535A/Y537A mutant IE86 protein is able to negatively autoregulate transcription from the major immediate-early (MIE) promoter and was recruited to the MIE promoter in a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. However, the P535A/Y537A mutant IE86 protein was unable to transactivate early viral genes and was not recruited to the early viral UL4 and UL112 promoters in a ChIP assay. From these data, we conclude that the transactivation and repressive functions of the HCMV IE86 protein can be separated and must occur through independent mechanisms.
Figures
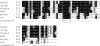



Similar articles
-
Functional properties of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein required for transcriptional regulation and virus replication.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8839-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00327-10. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20554773 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis by the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein is necessary for efficient virus replication.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(8):3872-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.8.3872-3883.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16571804 Free PMC article.
-
Separate DNA elements containing ATF/CREB and IE86 binding sites differentially regulate the human cytomegalovirus UL112-113 promoter at early and late times in the infection.J Virol. 1998 Apr;72(4):2697-707. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.4.2697-2707.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9525587 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of the human cytomegalovirus essential IE86 protein.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;325:133-52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-77349-8_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18637504 Review.
-
Activation and regulation of human cytomegalovirus early genes.Intervirology. 1996;39(5-6):361-77. doi: 10.1159/000150507. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 9130046 Review.
Cited by
-
Critical Role for the Human Cytomegalovirus Major Immediate Early Proteins in Recruitment of RNA Polymerase II and H3K27Ac To an Enhancer-Like Element in OriLyt.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0314422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03144-22. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36645269 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between mouse and human cytomegalovirus interactions with their respective hosts at immediate early times of the replication cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):241-9. doi: 10.1007/s00430-008-0078-1. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18264718 Review.
-
The cellular protein MCM3AP is required for inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis by the IE86 protein of human cytomegalovirus.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e45686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045686. Epub 2012 Oct 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23094019 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of the human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein required for transcriptional regulation and virus replication.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8839-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00327-10. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20554773 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Transcripts Encode Full-Length Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 and IE2 Proteins during Lytic Infection.J Virol. 2016 Sep 12;90(19):8855-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00741-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27466417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., C. J. Chiou, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Evaluation and mapping of the DNA binding and oligomerization domains of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus using yeast one and two hybrid interaction assays. Gene 210:25-36. - PubMed
-
- Asmar, J., L. Wiebusch, M. Truss, and C. Hagemeier. 2004. The putative zinc finger of the human cytomegalovirus IE2 86-kilodalton protein is dispensable for DNA binding and autorepression, thereby demarcating a concise core domain in the C terminus of the protein. J. Virol. 78:11853-11864. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bresnahan, W. A., T. Albrecht, and E. A. Thompson. 1998. The cyclin E promoter is activated by human cytomegalovirus 86-kDa immediate early protein. J. Biol. Chem. 273:22075-22082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

