Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD8+ cells produce transforming growth factor beta that can suppress HCV-specific T-cell responses
- PMID: 17376924
- PMCID: PMC1900307
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02202-06
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD8+ cells produce transforming growth factor beta that can suppress HCV-specific T-cell responses
Abstract
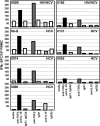
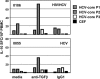
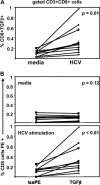
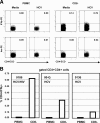
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific T-cell responses are rarely detected in peripheral blood, especially in the presence of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) coinfection. Based on recent evidence that T-regulatory cells may be increased in chronic HCV, we hypothesized that functional blockade of regulatory cells could raise HCV-specific responses and might be differentially regulated in the setting of HIV coinfection. Three groups of subjects were studied: HCV monoinfected, HCV-HIV coinfected, and healthy controls. Frequencies of peripheral T cells specific for peptides derived from HCV core, HIV type 1 p24, and recall antigens were analyzed by gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) enzyme-linked immuno-spot assay. HCV-specific T-cell responses were very weak in groups with HCV and HCV-HIV infections. Addition of blocking antibodies against transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1), -2, and -3 and interleukin-10 specifically increased the HCV-specific T-cell responses in both infected groups; however, this increase was attenuated in the group with HCV-HIV coinfection compared to HCV infection alone. No increase in recall antigen- or HIV-specific responses was observed. Flow cytometric sorter analysis demonstrated that regulatory-associated cytokines were produced by HCV-specific CD3(+)CD8(+)CD25(-) cells. Enhancement of the IFN-gamma effect was observed for both CD4 and CD8 T cells and was mediated primarily by TGF-beta1, -2, and -3 neutralization. In conclusion, blockade of TGF-beta secretion could enhance peripheral HCV-specific T-cell responses even in the presence of HIV coinfection.
Figures






References
-
- Alatrakchi, N., V. Di Martino, V. Thibault, and B. Autran. 2002. Strong CD4 Th1 responses to HIV and hepatitis C virus in HIV-infected long-term non-progressors co-infected with hepatitis C virus. AIDS 16:713-717. - PubMed
-
- Alatrakchi, N., V. Di Martino, V. Thibault, Y. Benhamou, C. Katlama, T. Poynard, and B. Autran. 2004. Decreased frequencies of virus-specific T helper type 1 cells during interferon alpha plus ribavirin treatment in HIV-hepatitis C virus co-infection. AIDS 18:121-123. - PubMed
-
- Alatrakchi, N., C. S. Graham, Q. He, K. E. Sherman, and M. J. Koziel. 2005. CD8+ cell responses to hepatitis C virus (HCV) in the liver of persons with HCV-HIV coinfection versus HCV monoinfection. J. Infect. Dis. 191:702-709. - PubMed
-
- Anthony, D. D., N. L. Yonkers, A. B. Post, R. Asaad, F. P. Heinzel, M. M. Lederman, P. V. Lehmann, and H. Valdez. 2004. Selective impairments in dendritic cell-associated function distinguish hepatitis C virus and HIV infection. J. Immunol. 172:4907-4916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

