Inhibition of recombinant N-type Ca(V) channels by the gamma 2 subunit involves unfolded protein response (UPR)-dependent and UPR-independent mechanisms
- PMID: 17376992
- PMCID: PMC6672476
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4566-06.2007
Inhibition of recombinant N-type Ca(V) channels by the gamma 2 subunit involves unfolded protein response (UPR)-dependent and UPR-independent mechanisms
Abstract
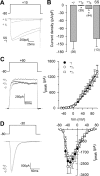
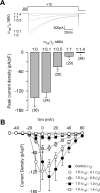
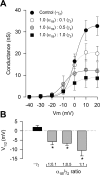
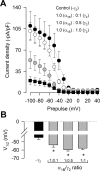
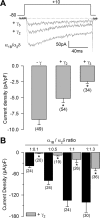
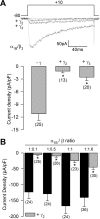
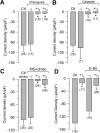
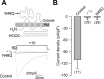
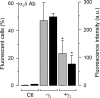
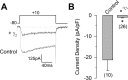
Auxiliary gamma subunits are an important component of high-voltage-activated calcium (Ca(V)) channels, but their precise regulatory role remains to be determined. In the current report, we have used complementary approaches including molecular biology and electrophysiology to investigate the influence of the gamma subunits on neuronal Ca(V) channel activity and expression. We found that coexpression of gamma2 or gamma3 subunits drastically inhibited macroscopic currents through recombinant N-type channels (Ca(V)2.2/beta3/alpha2delta) in HEK-293 cells. Using inhibitors of internalization, we found that removal of functional channels from the plasma membrane is an improbable mechanism of current regulation by gamma. Instead, changes in current amplitude could be attributed to two distinct mechanisms. First, gamma subunit expression altered the voltage dependence of channel activity. Second, gamma subunit expression reduced N-type channel synthesis via activation of the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Together, our findings (1) corroborate that neuronal gamma subunits significantly downregulate Ca(V)2.2 channel activity, (2) uncover a role for the gamma2 subunit in Ca(V)2.2 channel expression through early components of the biosynthetic pathway, and (3) suggest that, under certain conditions, channel protein misfolding could be induced by interactions with the gamma subunits, supporting the notion that Ca(V) channels constitute a class of difficult-to-fold proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Arikkath J, Campbell KP. Auxiliary subunits: essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:298–307. - PubMed
-
- Arikkath J, Chen CC, Ahern C, Allamand V, Flanagan JD, Coronado R, Gregg RG, Campbell KP. γ1 subunit interactions within the skeletal muscle L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:1212–1219. - PubMed
-
- Avila T, Andrade A, Felix R. Transforming growth factor-beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 downregulate CaV3.1 channel expression in mouse C2C12 myoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:448–456. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron. 1998;21:13–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
