5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway depends on Src activation but not on G protein or beta-arrestin signaling
- PMID: 17377064
- PMCID: PMC1877087
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-12-1080
5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptor activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway depends on Src activation but not on G protein or beta-arrestin signaling
Abstract
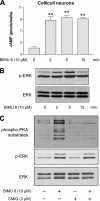
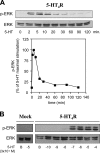
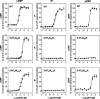
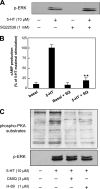
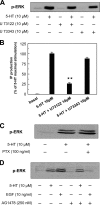
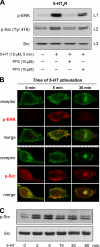
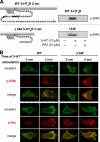
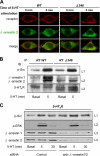
The 5-hydroxytryptamine(4) (5-HT(4)) receptors have recently emerged as key modulators of learning, memory, and cognitive processes. In neurons, 5-hydroxytryptamine(4) receptors (5-HT(4)Rs) activate cAMP production and protein kinase A (PKA); however, nothing is known about their ability to activate another key signaling pathway involved in learning and memory: the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Here, we show that 5-HT(4)R stimulation, in primary neurons, produced a potent but transient activation of the ERK pathway. Surprisingly, this activation was mostly PKA independent. Similarly, using pharmacological, genetic, and molecular tools, we observed that 5-HT(4)Rs in human embryonic kidney 293 cells, activated the ERK pathway in a G(s)/cAMP/PKA-independent manner. We also demonstrated that other classical G proteins (G(q)/G(i)/G(o)) and associated downstream messengers were not implicated in the 5-HT(4)R-activated ERK pathway. The 5-HT(4)R-mediated ERK activation seemed to be dependent on Src tyrosine kinase and yet totally independent of beta-arrestin. Immunocytofluorescence revealed that ERK activation by 5-HT(4)R was restrained to the plasma membrane, whereas p-Src colocalized with the receptor and carried on even after endocytosis. This phenomenon may result from a tight interaction between 5-HT(4)R and p-Src detected by coimmunoprecipitation. Finally, we confirmed that the main route by which 5-HT(4)Rs activate ERKs in neurons was Src dependent. Thus, in addition to classical cAMP/PKA signaling pathways, 5-HT(4)Rs may use ERK pathways to control memory process.
Figures

References
-
- Adamus G., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A. Genetic control of antibody response to bovine rhodopsin in mice: epitope mapping of rhodopsin structure. J. Neuroimmunol. 1991;34:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Banasr M., Hery M., Printemps R., Daszuta A. Serotonin-induced increases in adult cell proliferation and neurogenesis are mediated through different and common 5-HT receptor subtypes in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:450–460. - PubMed
-
- Baneres J. L., Mesnier D., Martin A., Joubert L., Dumuis A., Bockaert J. Molecular characterization of a purified 5-HT4 receptor: a structural basis for drug efficacy. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:20253–20260. - PubMed
-
- Barthet G., Gaven F., Framery B., Shinjo K., Nakamura T., Claeysen S., Bockaert J., Dumuis A. Uncoupling and endocytosis of 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 receptors. Distinct molecular events with different GRK2 requirements. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:27924–27934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

