In vitro expansion of erythroid progenitors from polycythemia vera patients leads to decrease in JAK2 V617F allele
- PMID: 17379069
- PMCID: PMC1931508
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2006.12.007
In vitro expansion of erythroid progenitors from polycythemia vera patients leads to decrease in JAK2 V617F allele
Abstract
Objectives: A G>T transversion in a tyrosine kinase JAK2 (V617F) was reported in over 80% of patients with polycythemia vera (PV). Current evidence suggests that JAK2(V617F) somatic mutation is involved in the pathogenesis of PV, as it confers erythropoietin-independent proliferation to erythroid progenitor cells. However, several unanswered questions regarding the essential role of JAK2(V617F) arose as 1) it is not a dominant mutation, 2) it is not PV-specific as it is found in several myeloproliferative disorders, and 3) some ( approximately 20%) PV patients lack the JAK2(V617F) mutation. We investigated the relative frequency of JAK2(V617F) in in vitro-expanded PV progenitors.
Methods: In vitro expansion of erythroid progenitors from mononuclear cells was optimized. Frequency of JAK2(V617F) allele was measured by using allele-specific real-time polymerase chain reaction. Clonality was performed using established procedure.
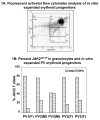
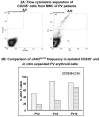
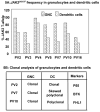
Results: In vitro expansion of PV erythroid progenitors and differentiated dendritic cells resulted in a decrease of the frequency of JAK2(V617F) allele compared with granulocytes or CD235(+) erythroid progenitors. Clonality analysis demonstrated that although granulocytes of these PV patients were clonal, expanded erythroid cells were polyclonal. However, in vitro-expanded PV erythroid progenitors still had approximately a twofold increased proliferative capacity in comparison with erythroid progenitors from healthy individuals. Erythropoietin favors the cells without JAK2(V617F) allele. Dendritic cells in one out of three patients remained clonal.
Conclusion: JAK2(V617F) mutation does not provide a proliferative/survival advantage to the PV clone during in vitro expansion. These data suggest that the JAK2(V617F) mutation plays an important role in the biology of PV, yet it may not be the PV-initiating event.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The JAK kinase inhibitor CP-690,550 suppresses the growth of human polycythemia vera cells carrying the JAK2V617F mutation.Cancer Sci. 2008 Jun;99(6):1265-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00817.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18482053 Free PMC article.
-
Polycythemia vera is not initiated by JAK2V617F mutation.Exp Hematol. 2007 Jan;35(1):32-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2006.11.012. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17198871
-
Imatinib effect on growth and signal transduction in polycythemia vera.Exp Hematol. 2007 Jun;35(6):931-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.03.012. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17533047
-
Polycythemia vera: scientific advances and current practice.Semin Hematol. 2005 Oct;42(4):206-20. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2005.08.003. Semin Hematol. 2005. PMID: 16210034 Review.
-
Current diagnostic criteria for the chronic myeloproliferative disorders (MPD) essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV) and chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (CIMF).Pathol Biol (Paris). 2007 Mar;55(2):92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2006.06.002. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2007. PMID: 16919893 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical characterization of atiprimod, a novel JAK2 AND JAK3 inhibitor.Invest New Drugs. 2011 Oct;29(5):818-26. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9429-z. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Invest New Drugs. 2011. PMID: 20372971 Free PMC article.
-
Extent of hematopoietic involvement by TET2 mutations in JAK2V⁶¹⁷F polycythemia vera.Haematologica. 2011 May;96(5):775-8. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.029678. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Haematologica. 2011. PMID: 21273266 Free PMC article.
-
The JAK kinase inhibitor CP-690,550 suppresses the growth of human polycythemia vera cells carrying the JAK2V617F mutation.Cancer Sci. 2008 Jun;99(6):1265-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00817.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18482053 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential treatment of CD34+ cells from patients with primary myelofibrosis with chromatin-modifying agents eliminate JAK2V617F-positive NOD/SCID marrow repopulating cells.Blood. 2010 Dec 23;116(26):5972-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-269696. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20858855 Free PMC article.
-
Study of two tyrosine kinase inhibitors on growth and signal transduction in polycythemia vera.Exp Hematol. 2007 Nov;35(11):1647-56. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.08.018. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17976517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spivak JL. The chronic myeloproliferative disorders: clonality and clinical heterogeneity. Semin Hematol. 2004;41:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Najfeld V, Montella A, Scalise T, et al. Exploring polycythemia vera with fluorescence in situ hybridization: additional cryptic 9p is the most frequent abnormality detected. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:558–566. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Guan Y, Prchal JT. Acquired uniparental disomy of chromosome 9p is a frequent stem cell defect in polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:229–236. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signaling causes polycythemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera. Cancer Cell. 2005;4:387–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

