Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 on transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 and NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 17379600
- PMCID: PMC2048714
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M700156200
Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 on transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 and NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
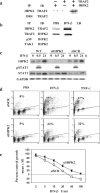
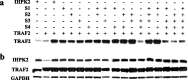
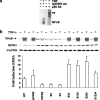
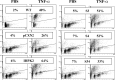
We previously showed that inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (IHPK2) functions as a growth-suppressive and apoptosis-enhancing kinase during cell stress. Overexpression of IHPK2 sensitized ovarian carcinoma cell lines to the growth-suppressive and apoptotic effects of interferon beta (IFN-beta), IFN-alpha2, and gamma-irradiation. Expression of a kinase-dead mutant abrogated 50% of the apoptosis induced by IFN-beta. Because the kinase-dead mutant retained significant response to cell stressors, we hypothesized that a portion of the death-promoting function of IHPK2 was independent of its kinase activity. We now demonstrate that IHPK2 binds to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 2 and interferes with phosphorylation of transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), thereby inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. IHPK2 contains two sites required for TRAF2 binding, Ser-347 and Ser-359. Compared with wild type IHPK2-transfected cells, cells expressing S347A and S359A mutations displayed 3.5-fold greater TAK1 activation following TNF-alpha. This mutant demonstrated a 6-10-fold increase in NF-kappaB DNA binding following TNF-alpha compared with wild type IHPK2-expressing cells in which NF-kappaB DNA binding was inhibited. Cells transfected with wild type IHPK2 or IHPK2 mutants that lacked S347A and S359A mutations displayed enhanced terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling staining following TNF-alpha. We believe that IHPK2-TRAF2 binding leads to attenuation of TAK1- and NF-kappaB-mediated signaling and is partially responsible for the apoptotic activity of IHPK2.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Apo2L/TRAIL induction and nuclear translocation of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 during IFN-beta-induced apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma.Biochem J. 2005 Jan 15;385(Pt 2):595-603. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040971. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15634191 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine 63-linked polyubiquitination of TAK1 at lysine 158 is required for tumor necrosis factor alpha- and interleukin-1beta-induced IKK/NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5347-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076976. Epub 2009 Dec 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20038579 Free PMC article.
-
Xenopus death-domain-containing proteins FADD and RIP1 synergistically activate JNK and NF-kappaB.Biol Cell. 2006 Aug;98(8):465-78. doi: 10.1042/BC20050091. Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16597320
-
IRF-1 inhibits NF-κB activity, suppresses TRAF2 and cIAP1 and induces breast cancer cell specific growth inhibition.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(7):1029-41. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1046646. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26011589 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
Cited by
-
The inositol pyrophosphate pathway in health and diseases.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018 May;93(2):1203-1227. doi: 10.1111/brv.12392. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018. PMID: 29282838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates: Signaling Molecules with Pleiotropic Actions in Mammals.Molecules. 2020 May 8;25(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092208. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32397291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Casein kinase-2 mediates cell survival through phosphorylation and degradation of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase-2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 8;108(6):2205-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019381108. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21262846 Free PMC article.
-
The enzymes of human diphosphoinositol polyphosphate metabolism.FEBS J. 2014 Jan;281(1):14-33. doi: 10.1111/febs.12575. Epub 2013 Nov 5. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24152294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates: structure, enzymology and function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Dec;66(24):3851-71. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0115-2. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19714294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saiardi A., Bhandari R., Resnick A.C., Snowman A.M., Snyder S.H. Science. 2004;306:2101–2105. - PubMed
-
- Luo H.R., Huang Y.E., Chen J.C., Saiardi A., Iijima M., Ye K., Huang Y., Nagata E., Devreotes P., Snyder S.H. Cell. 2003;114:559–572. - PubMed
-
- Hanakahi L.A., Bartlet-Jones M., Chappell C., Pappin D., West S.C. Cell. 2000;102:721–729. - PubMed
-
- Ma Y., Lieber M.R. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;30:30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

