Structure and enzymatic functions of human CD38
- PMID: 17380198
- PMCID: PMC1829193
- DOI: 10.2119/2006–00086.Lee
Structure and enzymatic functions of human CD38
Abstract
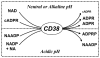
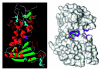
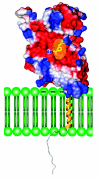
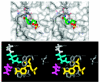
CD38 is a novel multifunctional protein that serves not only as an antigen but also as an enzyme. It catalyzes the metabolism of cyclic ADP-ribose and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate, two structurally and functionally distinct Ca(2+) messengers targeting, respectively, the endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomal Ca(2+) stores. The protein has recently been crystallized and its three-dimensional structure solved to a resolution of 1.9 A. The crystal structure of a binary complex reveals critical interactions between residues at the active site and a bound substrate, providing mechanistic insights to its novel multi-functional catalysis. This article reviews the current advances in the understanding of the structural determinants that control the multiple enzymatic reactions catalyzed by CD38.
Figures
References
-
- Malavasi F, et al. CD38: a multi-lineage cell activation molecule with a split personality. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1992;22:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Malavasi F, et al. Human CD38: a glycoprotein in search of a function. Immunol Today. 1994;15:95–97. - PubMed
-
- Mehta K, Shahid U, Malavasi F. Human CD38, a cell-surface protein with multiple functions. FASEB J. 1996;10:1408–17. - PubMed
-
- Takasawa S, et al. Synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose by human leukocyte antigen CD38 and inhibition of the hydrolysis by ATP. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:26052–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
