T-box factors determine cardiac design
- PMID: 17380306
- PMCID: PMC2778635
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-007-6518-z
T-box factors determine cardiac design
Abstract
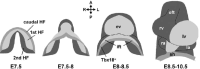
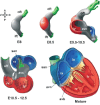
The heart of higher vertebrates is a structurally complicated multi-chambered pump that contracts synchronously. For its proper function a number of distinct integrated components have to be generated, including force-generating compartments, unidirectional valves, septa and a system in charge of the initiation and coordinated propagation of the depolarizing impulse over the heart. Not surprisingly, a large number of regulating factors are involved in these processes that act in complex and intertwined pathways to regulate the activity of target genes responsible for morphogenesis and function. The finding that mutations in T-box transcription factor-encoding genes in humans lead to congenital heart defects has focused attention on the importance of this family of regulators in heart development. Functional and genetic analyses in a variety of divergent species has demonstrated the critical roles of multiple T-box factor gene family members, including Tbx11, -2, -3, -5, -18 and -20, in the patterning, recruitment, specification, differentiation and growth processes underlying formation and integration of the heart components. Insight into the roles of T-box factors in these processes will enhance our understanding of heart formation and the underlying molecular regulatory pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
T-box factors: insights into the evolutionary emergence of the complex heart.Ann Med. 2012 Nov;44(7):680-93. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2011.607468. Epub 2011 Sep 19. Ann Med. 2012. PMID: 21923612 Review.
-
Murine T-box transcription factor Tbx20 acts as a repressor during heart development, and is essential for adult heart integrity, function and adaptation.Development. 2005 May;132(10):2451-62. doi: 10.1242/dev.01799. Epub 2005 Apr 20. Development. 2005. PMID: 15843414
-
Mechanisms of T-box gene function in the developing heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jul 15;91(2):212-22. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr112. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21498422 Review.
-
T-box genes and cardiac development.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003 Feb;69(1):25-37. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.10001. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003. PMID: 12768655 Review.
-
Msx1 and Msx2 are functional interacting partners of T-box factors in the regulation of Connexin43.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Jun 1;78(3):485-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn049. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18285513
Cited by
-
Heart chamber size in zebrafish is regulated redundantly by duplicated tbx2 genes.Dev Dyn. 2011 Jun;240(6):1548-57. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22622. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21448936 Free PMC article.
-
Tbx3 is required for outflow tract development.Circ Res. 2008 Sep 26;103(7):743-50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.172858. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18723448 Free PMC article.
-
The Transitional Heart: From Early Embryonic and Fetal Development to Neonatal Life.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2020;47(5):373-386. doi: 10.1159/000501906. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 31533099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying the cardiac pacemaker: the role of SK4 calcium-activated potassium channels.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Jan;37(1):82-97. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.135. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26725737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specification of the cardiac conduction system by transcription factors.Circ Res. 2009 Sep 25;105(7):620-30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.204123. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19797194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moorman A.F.M., Christoffels V.M. Cardiac Chamber Formation: Development, genes and evolution. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83:1223–1267. - PubMed
-
- Brand T. Heart development: molecular insights into cardiac specification and early morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2003;258:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Buckingham M., Meilhac S., Zaffran S. Building the mammalian heart from two sources of myocardial cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:826–837. - PubMed
-
- Campbell C., Goodrich K., Casey G., Beatty B. Cloning and mapping of a human gene (TBX2) sharing a highly conserved protein motif with the Drosophila omb gene. Genomics. 1995;28:255–260. - PubMed
-
- Law D.J., Gebuhr T., Garvey N., Agulnik S.I., Silver L.M. Identification, characterization, and localization to chromosome 17q21-22 of the human TBX2 homolog, member of a conserved developmental gene family. Mamm. Genome. 1995;6:793–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

