Cyclodextrin, a probe for studying adhesive interactions
- PMID: 17382373
- PMCID: PMC1988679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acthis.2007.02.004
Cyclodextrin, a probe for studying adhesive interactions
Abstract
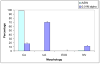
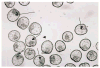
In this short communication, we introduce alpha-cyclodextrin as a new probe to study mechanisms of adhesive interactions. We show that this cyclic polysaccharide, that consisting of six glucosyl residues linked by alpha-1,4 bonds, was the only sugar of 22 tested that dramatically blocked a specific cellular interaction in the sea urchin embryo (p<0.001 compared with non-sugar controls). A total of 150-400 embryos were sampled for each concentration of each sugar tested. Mechanisms of cellular interactions have been studied for almost a century and they still remain poorly understood. Cyclodextrin is an exciting new tool that can be utilized for investigating these mechanisms.
Figures

References
-
- Akasaka K, Amemiya S, Terayama H. Scanning electron microscopical study of the inside of sea urchin (Pseudocentrotus depressus): Effects of aryl beta-xyloside, tunicamycin, and deprivation of sulfate ions. Exp Cell Res. 1980;129:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Bidwell JP, Spotte S. Artificial Seawaters, Formulas and Methods. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Inc.; Boston: 1985. p. 256.
-
- Blackburn C, Schnaar R. Carbohydrate-specific cell adhesion is mediated by immobilized glycolipids. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1983;258:1180–1188. - PubMed
-
- Cambry I, Le Mercier M, Lefranc F, Kiss R. Galactin-1: a small protein with major functions. Glycobiology. 2006;16:137R–157R. - PubMed
-
- Davidson EH. The sea urchin genome: where will it lead us? Science. 2006;314:939–940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

