Carbenoxolone modifies spontaneous inhibitory and excitatory synaptic transmission in rat somatosensory cortex
- PMID: 17382470
- PMCID: PMC1934620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.01.042
Carbenoxolone modifies spontaneous inhibitory and excitatory synaptic transmission in rat somatosensory cortex
Abstract
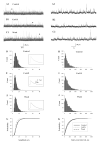
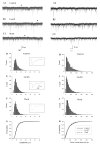
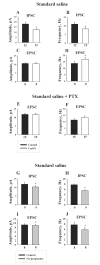
Gap junction (GJ) coupling between neocortical GABAergic interneurons plays a critical role in the synchronization of activity in cortical networks in physiological and pathophysiological states, e.g., seizures. Past studies have shown that GJ blockers exert anticonvulsant actions in both in vivo and in vitro models of epilepsy. However, the precise mechanisms underlying these antiepileptic effects have not been fully elucidated. This is due, in part, to a lack of information of the influence of GJ blockade on network activity in the absence of convulsant agents or enhanced neuronal excitation. One key question is whether GJ blockers act on excitatory or inhibitory systems, or both. To address this issue, we examined the effects of the GJ blocker carbenoxolone (CarbX, 150 microM) on spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) and excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) in acute slices of rat somatosensory cortex. Results showed that CarbX decreased the amplitude and frequency of sIPSCs by 30.2% and 25.7%, respectively. CarbX increased the mean frequency of sEPSCs by 24.1%, but had no effect on sEPSC amplitude. During blockade of GABAA-mediated events with picrotoxin (20 microM), CarbX induced only a small increase in sEPSC frequency that was not statistically different from control, indicating CarbX enhancement of sEPECs was secondary to the depression of synaptic inhibition. These findings suggest that in neocortex, blockade of GJs leads to an increase in spontaneous excitation by uncoupling GABAergic interneurons, and that electronic communication between inhibitory cells plays a significant role in regulating tonic synaptic excitation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of synaptic input to hypothalamic presympathetic neurons by GABA(B) receptors.Neuroscience. 2006 Oct 13;142(2):595-606. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.039. Epub 2006 Aug 2. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16887273
-
Propagation of postsynaptic currents and potentials via gap junctions in GABAergic networks of the rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 15;578(Pt 2):527-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123463. Epub 2006 Nov 16. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17110410 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prostaglandin E2 on synaptic transmission in the rat spinal trigeminal subnucleus caudalis.Brain Res. 2015 Nov 2;1625:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.08.024. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26320551
-
Modulation of allopregnanolone on excitatory transmitters release from single glutamatergic terminal.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Apr;93:39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23174309 Review.
-
[Methods for in vivo patch-clamp recordings and their applications: synaptic responses in somatosensory cortex].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006 Dec;128(6):381-7. doi: 10.1254/fpj.128.381. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 17167211 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous activity in the developing gerbil auditory cortex in vivo involves GABAergic transmission.Neuroscience. 2012 Dec 13;226:130-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.09.008. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22986170 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-hippocampal injection of lipopolysaccharide inhibits kindled seizures and retards kindling rate in adult rats.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Apr;226(1):107-20. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3415-6. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23371749
-
Direct actions of carbenoxolone on synaptic transmission and neuronal membrane properties.J Neurophysiol. 2009 Aug;102(2):974-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.00060.2009. Epub 2009 Jun 17. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19535488 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junctions modulate seizures in a mean-field model of general anesthesia for the cortex.Cogn Neurodyn. 2012 Jun;6(3):215-25. doi: 10.1007/s11571-012-9194-0. Epub 2012 Mar 2. Cogn Neurodyn. 2012. PMID: 23730353 Free PMC article.
-
Consciousness is supported by near-critical slow cortical electrodynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Feb 15;119(7):e2024455119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024455119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35145021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benardo LS. Recruitment of GABAergic inhibition and synchronization of inhibitory interneurons in rat neocortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1997;77:3134–3144. - PubMed
-
- Chagnac-Amitai Y, Connors BW. Horizontal spread of synchronized activity in neocortex and its control by GABA-mediated inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 1989;61:747–758. - PubMed
-
- Colling SB, Man WD, Draguhn A, Jefferys JG. Dendritic shrinkage and dye-coupling between rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in the tetanus toxin model of epilepsy. Brain Res. 1996;741:38–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

