AU-rich-element-mediated upregulation of translation by FXR1 and Argonaute 2
- PMID: 17382880
- PMCID: PMC3430382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.038
AU-rich-element-mediated upregulation of translation by FXR1 and Argonaute 2
Abstract
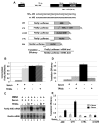
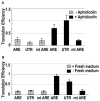
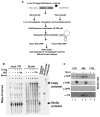
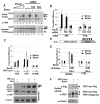
AU-rich elements (AREs), present in mRNA 3'-UTRs, are potent posttranscriptional regulatory signals that can rapidly effect changes in mRNA stability and translation, thereby dramatically altering gene expression with clinical and developmental consequences. In human cell lines, the TNFalpha ARE enhances translation relative to mRNA levels upon serum starvation, which induces cell-cycle arrest. An in vivo crosslinking-coupled affinity purification method was developed to isolate ARE-associated complexes from activated versus basal translation conditions. We surprisingly found two microRNP-related proteins, fragile-X-mental-retardation-related protein 1 (FXR1) and Argonaute 2 (AGO2), that associate with the ARE exclusively during translation activation. Through tethering and shRNA-knockdown experiments, we provide direct evidence for the translation activation function of both FXR1 and AGO2 and demonstrate their interdependence for upregulation. This novel cell-growth-dependent translation activation role for FXR1 and AGO2 allows new insights into ARE-mediated signaling and connects two important posttranscriptional regulatory systems in an unexpected way.
Figures
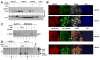
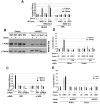

Comment in
-
Argonautes and company: sailing against the wind.Cell. 2007 Mar 23;128(6):1027-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.033. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17382873
References
-
- Andersson K, Sundler R. Signalling to translational activation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha expression in human THP-1 cells. Cytokine. 2000;12:1784–1787. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:135–141. - PubMed
-
- Baron-Benhamou J, Gehring NH, Kulozik AE, Hentze MW. Using the lambdaN peptide to tether proteins to RNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2004;257:135–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

