Vik1 modulates microtubule-Kar3 interactions through a motor domain that lacks an active site
- PMID: 17382884
- PMCID: PMC1987336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.046
Vik1 modulates microtubule-Kar3 interactions through a motor domain that lacks an active site
Abstract
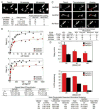
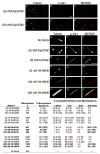
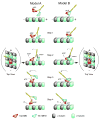
Conventional kinesin and class V and VI myosins coordinate the mechanochemical cycles of their motor domains for processive movement of cargo along microtubules or actin filaments. It is widely accepted that this coordination is achieved by allosteric communication or mechanical strain between the motor domains, which controls the nucleotide state and interaction with microtubules or actin. However, questions remain about the interplay between the strain and the nucleotide state. We present an analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Kar3/Vik1, a heterodimeric C-terminal Kinesin-14 containing catalytic Kar3 and the nonmotor protein Vik1. The X-ray crystal structure of Vik1 exhibits a similar fold to the kinesin and myosin catalytic head, but lacks an ATP binding site. Vik1 binds more tightly to microtubules than Kar3 and facilitates cooperative microtubule decoration by Kar3/Vik1 heterodimers, and yet allows motility. These results demand communication between Vik1 and Kar3 via a mechanism that coordinates their interactions with microtubules.
Figures




Comment in
-
Kinesin Kar3 and Vik1 go head to head.Cell. 2007 Mar 23;128(6):1033-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.003. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17382876
References
-
- Bond CS. TopDraw: a sketchpad for protein structure topology cartoons. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:311–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

