The intricate world of riboswitches
- PMID: 17383225
- PMCID: PMC1894890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.006
The intricate world of riboswitches
Abstract
Riboswitches are segments of the 5'-untranslated region of certain bacterial mRNAs that upon recognition of specific ligands modify the expression of a protein(s) encoded in the message. These proteins are responsible for the biosynthesis or transport of ligands, which are typically organic molecules but could also be metal ions. Riboswitch-mediated control of gene expression might be thermodynamic or kinetic, depending on the rate of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase and the structures adopted by the riboswitch RNA. Certain 5'-untranslated regions harbor two riboswitches in tandem that bind to different ligands. Thus, RNA sensors can respond to metabolic changes by modifying gene expression in ways previously thought to be exclusive of proteins.
Figures
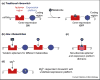
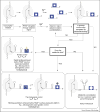
References
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by riboswitches. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Tucker BJ, Breaker RR. Riboswitches as versatile gene control elements. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005;15:342–348. - PubMed
-
-
Thore S, Leibundgut M, Ban N. Structure of the eukaryotic thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch with its regulatory ligand. Science. 2006;312:1208–1211.The recently published TPP riboswitch crystal structure, which provides mechanistic information on riboswitch folding and antibiotic resistance.
-
-
-
Serganov A, Polonskaia A, Phan AT, Breaker RR, Patel DJ. Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch. Nature. 2006;441:1167–1171.The recently published TPP riboswitch crystal structure is complemented by enzymatic probing data.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

