Comprehensive esophageal microscopy by using optical frequency-domain imaging (with video)
- PMID: 17383652
- PMCID: PMC2705339
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.08.009
Comprehensive esophageal microscopy by using optical frequency-domain imaging (with video)
Abstract
Background: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has been used for high-resolution endoscopic imaging and diagnosis of specialized intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and intramucosal carcinoma of the esophagus. However, the relatively slow image-acquisition rate of the present OCT systems inhibits wide-field imaging and limits the clinical utility of OCT for diagnostic imaging in patients with Barrett's esophagus.
Objective: This study describes a new optical imaging technology, optical frequency-domain imaging (OFDI), derived from OCT, that enables comprehensive imaging of large esophageal segments with microscopic resolution.
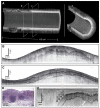
Design: A prototype OFDI system was developed for endoscopic imaging. The system was used in combination with a balloon-centering catheter to comprehensively image the distal esophagus in swine.
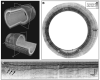
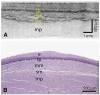
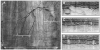
Results: Volumetric images of the mucosa and portions of the muscularis propria were obtained for 4.5-cm-long segments. Image resolution was 7 microm in depth and 30 microm parallel to the lumen, and provided clear delineation of each mucosal layer. The 3-dimensional data sets were used to create cross-sectional microscopic images, as well as vascular maps of the esophagus. Submucosal vessels and capillaries were visualized by using Doppler-flow processing.
Conclusions: Comprehensive microscopic imaging of the distal esophagus in vivo by using OFDI is feasible. The unique capabilities of this technology for obtaining detailed information of tissue microstructure over large mucosal areas may open up new possibilities for improving the management of patients with Barrett's esophagus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive microscopy of the esophagus in human patients with optical frequency domain imaging.Gastrointest Endosc. 2008 Oct;68(4):745-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.014. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008. PMID: 18926183 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography of Barrett's esophagus: preliminary descriptive clinical study correlating images with histology.Endoscopy. 2007 Jul;39(7):599-605. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-966648. Endoscopy. 2007. PMID: 17611914
-
Optical coherence tomography: advanced technology for the endoscopic imaging of Barrett's esophagus.Endoscopy. 2000 Dec;32(12):921-30. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-9626. Endoscopy. 2000. PMID: 11147939
-
Future of diagnosing neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus: volumetric laser endomicroscopy.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun;11(3):179-183. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0863-3. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29680981 Review.
-
Diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus using optical coherence tomography.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2003 Apr;13(2):309-23. doi: 10.1016/s1052-5157(03)00012-6. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2003. PMID: 12916662 Review.
Cited by
-
Laser tissue coagulation and concurrent optical coherence tomography through a double-clad fiber coupler.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 Mar 16;6(4):1293-303. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.001293. eCollection 2015 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 25909013 Free PMC article.
-
Optical endomicroscopy and the road to real-time, in vivo pathology: present and future.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Aug 13;7:98. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-98. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22889003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophageal OCT Imaging Using a Paddle Probe Externally Attached to Endoscope.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Oct;67(10):4805-4812. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-07372-w. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35084606 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic optical coherence tomography angiography microvascular features associated with dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus (with video).Gastrointest Endosc. 2017 Sep;86(3):476-484.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.01.034. Epub 2017 Feb 5. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017. PMID: 28167119 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic 3D reconstruction of an anatomically correct upper airway from endoscopic long range OCT images.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Aug 10;14(9):4594-4608. doi: 10.1364/BOE.496812. eCollection 2023 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37791278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tearney GJ, Brezinski ME, Bouma BE, et al. In vivo endoscopic optical biopsy with optical coherence tomography. Science. 1997;276:2037–9. - PubMed
-
- Sergeev A, Gelikonov V, Gelikonov G, et al. In vivo endoscopic OCT imaging of precancer and cancer states of human mucosa. Opt Express. 1997;1:432–40. - PubMed
-
- Bouma BE, Tearney GJ. Power-efficient nonreciprocal interferometer and linear-scanning fiber-optic catheter for optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 1999;24:531–3. - PubMed
-
- Bouma BE, Tearney GJ, Compton CC, et al. High-resolution imaging of the human esophagus and stomach in vivo using optical coherence tomography. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51:467–74. - PubMed
-
- Sivak MV, Kobayashi K, Izatt JA, et al. High-resolution endoscopic imaging of the GI tract using optical coherence tomography. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51:474–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

