Improperly terminated, unpolyadenylated mRNA of sense transgenes is targeted by RDR6-mediated RNA silencing in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17384170
- PMCID: PMC1867362
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.045724
Improperly terminated, unpolyadenylated mRNA of sense transgenes is targeted by RDR6-mediated RNA silencing in Arabidopsis
Abstract
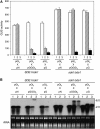
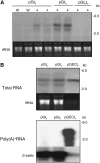
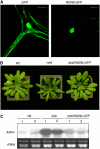
RNA silencing can be induced by highly transcribed transgenes through a pathway dependent on RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE6 (RDR6) and may function as a genome protection mechanism against excessively expressed genes. Whether all transcripts or just aberrant transcripts activate this protection mechanism is unclear. Consistent RNA silencing induced by a transgene with three direct repeats of the beta-glucuronidase (GUS) open reading frame (ORF) is associated with high levels of truncated, unpolyadenylated transcripts, probably from abortive transcription elongation. Truncated, unpolyadenylated transcripts from triple GUS ORF repeats were degraded in the wild type but accumulated in an rdr6 mutant, suggesting targeting for degradation by RDR6-mediated RNA silencing. A GUS transgene without a 3' transcription terminator produced unpolyadenylated readthrough mRNA and consistent RDR6-dependent RNA silencing. Both GUS triple repeats and terminator-less GUS transgenes silenced an expressed GUS transgene in trans in the wild type but not in the rdr6 mutant. Placing two 3' terminators in the GUS transgene 3' reduced mRNA 3' readthrough, decreased GUS-specific small interfering RNA accumulation, and enhanced GUS gene expression. Moreover, RDR6 was localized in the nucleus. We propose that improperly terminated, unpolyadenylated mRNA from transgene transcription is subject to RDR6-mediated RNA silencing, probably by acting as templates for the RNA polymerase, in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interconnections between mRNA degradation and RDR-dependent siRNA production in mRNA turnover in plants.J Plant Res. 2017 Mar;130(2):211-226. doi: 10.1007/s10265-017-0906-8. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 28197782 Review.
-
The Arabidopsis DCP2 gene is required for proper mRNA turnover and prevents transgene silencing in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2012 Nov;72(3):368-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05066.x. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22639932
-
High-efficiency silencing of a beta-glucuronidase gene in rice is correlated with repetitive transgene structure but is independent of DNA methylation.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 May;43(1):67-82. doi: 10.1023/a:1006490331303. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10949375
-
Silencing of invertedly repeated transgenes in Arabidopsis thaliana.Meded Rijksuniv Gent Fak Landbouwkd Toegep Biol Wet. 2001;66(3b):393-9. Meded Rijksuniv Gent Fak Landbouwkd Toegep Biol Wet. 2001. PMID: 15954624
-
Plant terminators: the unsung heroes of gene expression.J Exp Bot. 2023 Apr 9;74(7):2239-2250. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac467. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36477559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for antisense transcription associated with microRNA target mRNAs in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2009 Apr;5(4):e1000457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000457. Epub 2009 Apr 17. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19381263 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of the transient expression system for production of recombinant proteins in plants.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 19;8(1):4755. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23024-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29555968 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA deep sequencing reveals role for Arabidopsis thaliana RNA-dependent RNA polymerases in viral siRNA biogenesis.PLoS One. 2009;4(3):e4971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004971. Epub 2009 Mar 24. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19308254 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and genetic requirements for the biogenesis of tobacco rattle virus-derived small interfering RNAs.J Virol. 2008 Jun;82(11):5167-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00272-08. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18353962 Free PMC article.
-
Interconnections between mRNA degradation and RDR-dependent siRNA production in mRNA turnover in plants.J Plant Res. 2017 Mar;130(2):211-226. doi: 10.1007/s10265-017-0906-8. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 28197782 Review.
References
-
- Adamson, T.E., Shutt, D.C., and Price, D.H. (2005). Functional coupling of cleavage and polyadenylation with transcription of mRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 280 32262–32271. - PubMed
-
- Allen, E., Xie, Z., Gustafson, A.M., and Carrington, J.C. (2005). microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121 207–221. - PubMed
-
- Baker, K.E., and Parker, R. (2004). Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Terminating erroneous gene expression. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16 293–299. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe, D. (2004). RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431 356–363. - PubMed
-
- Beclin, C., Boutet, S., Waterhouse, P., and Vaucheret, H. (2002). A branched pathway for transgene-induced RNA silencing in plants. Curr. Biol. 12 684–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

