A combined structural dynamics approach identifies a putative switch in factor VIIa employed by tissue factor to initiate blood coagulation
- PMID: 17384232
- PMCID: PMC2203332
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.062504907
A combined structural dynamics approach identifies a putative switch in factor VIIa employed by tissue factor to initiate blood coagulation
Abstract
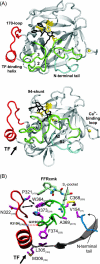
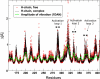
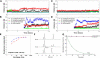
Coagulation factor VIIa (FVIIa) requires tissue factor (TF) to attain full catalytic competency and to initiate blood coagulation. In this study, the mechanism by which TF allosterically activates FVIIa is investigated by a structural dynamics approach that combines molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and hydrogen/deuterium exchange (HX) mass spectrometry on free and TF-bound FVIIa. The differences in conformational dynamics from MD simulations are shown to be confined to regions of FVIIa observed to undergo structural stabilization as judged by HX experiments, especially implicating activation loop 3 (residues 365-374{216-225}) of the so-called activation domain and the 170-loop (residues 313-322{170A-175}) succeeding the TF-binding helix. The latter finding is corroborated by experiments demonstrating rapid deglycosylation of Asn322 in free FVIIa by PNGase F but almost complete protection in the presence of TF or an active-site inhibitor. Based on MD simulations, a key switch of the TF-induced structural changes is identified as the interacting pair Leu305{163} and Phe374{225} in FVIIa, whose mutual conformations are guided by the presence of TF and observed to be closely linked to the structural stability of activation loop 3. Altogether, our findings strongly support an allosteric activation mechanism initiated by the stabilization of the Leu305{163}/Phe374{225} pair, which, in turn, stabilizes activation loop 3 and the S(1) and S(3) substrate pockets, the activation pocket, and N-terminal insertion.
Figures


References
-
- Bajaj S.P., Schmidt, A.E., Agah, S., Bajaj, M.S., and Padmanabhan, K. 2006. High resolution structures of p-aminobenzamidine- and benzamidine-VIIa/soluble tissue factor: Unpredicted conformation of the 192–193 peptide bond and mapping of Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and Zn2+ sites in factor VIIa. J. Biol. Chem. 281: 24873–24888. - PubMed
-
- Banner D.W., D'Arcy, A., Chène, C., Winkler, F.K., Guha, A., Konigsberg, W.H., Nemerson, Y., and Kirchhofer, D. 1996. The crystal structure of the complex of blood coagulation factor VIIa with soluble tissue factor. Nature 380: 41–46. - PubMed
-
- Davie E.W., Fujikawa, K., and Kisiel, W. 1991. The coagulation cascade: Initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 30: 10363–10370. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

