The role of optic nerve ultrasonography in the diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure
- PMID: 17384377
- PMCID: PMC2658229
- DOI: 10.1136/emj.2006.040931
The role of optic nerve ultrasonography in the diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the convenience and utility of optic nerve ultrasonography (ONUS) in the evaluation of emergency patients with elevated intracranial pressure (EICP) due to traumatic or non-traumatic causes.
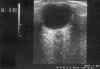
Methods: This study was conducted between May 2005 and December 2005 in the emergency department of Meram Faculty of Medicine, Selcuk University. Patients with traumatic or non-traumatic EICP were included in the study. Among these, 28 patients with EICP determined on cranial computed tomography (CCT) and a control group of 26 patients with no disease had the vertical and horizontal diameters of the optic nerves (ONs) of both eyes measured by ultrasonography (US). The measurements were done by wetting the closed eyelids and using a 7.5-MHz linear probe.
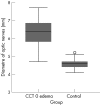
Results: Horizontal and vertical diameters of both ONs of the 54 patients were measured and the averages calculated. The mean (SD) ON diameter for the group suspected of having EICP was found to be 6.4 (0.7) mm, and that for the control group to be 4.6 (0.3) mm. In the statistical analysis carried out between these two groups (t test), the difference was found to be significant at p<0.001.
Conclusions: In detection and follow-up of EICP cases, such as cerebrovascular accident and trauma, ONUS is a practical, risk-free, inexpensive, convenient and, if performed by experts, reliable method. As a result, although CCT may be more useful in diagnosis, ONUS may be more efficient in detecting EICP. In those cases where CCT and other conventional imaging methods are not available, ONUS can facilitate the diagnosis and help in treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Hayreh M S, Hayreh S S. Optic disc edema in raised intracranial pressure. I. Evolution and resolution. Arch Ophthalmol 1977951237–1244. - PubMed
-
- Hayreh S S. Optic disc edema in raised intracranial pressure. V. Pathogenesis. Arch Ophthalmol 1977951553–1565. - PubMed
-
- Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski P R. Elevated intracranial pressure detected by bedside emergency ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath. Acad Emerg Med 200310376–381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous