Mechanisms involved in the regulation of mRNA for M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and endothelial and neuronal NO synthases in rat atria
- PMID: 17384670
- PMCID: PMC2013945
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707180
Mechanisms involved in the regulation of mRNA for M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and endothelial and neuronal NO synthases in rat atria
Abstract
Background and purpose: Agonists of the M(2) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) increase mRNA for this receptor and mRNA for endothelial and neuronal isoforms of NO synthase (eNOS or nNOS). Here we examine the different signalling pathways involved in such events in rat cardiac atria.
Experimental approach: In isolated atria, the effects of carbachol on mRNA for M(2) receptors, eNOS and nNOS were measured along with changes in phosphoinositide (PI) turnover, translocation of protein kinase C (PKC), NOS activity and atrial contractility.
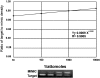
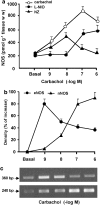
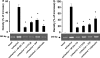
Key results: Carbachol increased mRNA for M(2) receptors, activation of PI turnover, translocation of PKC and NOS activity and decreased atrial contractility. Inhibitors of phospholipase C (PLC), calcium/calmodulin (CaM), NOS and PKC prevented the carbachol-dependent increase in mRNA for M(2) receptors. These inhibitors also attenuated the carbachol induced increase in nNOS- and eNOS-mRNA levels. Inhibition of nNOS shifted the dose response curve of carbachol on contractility to the right, whereas inhibition of eNOS shifted it to the left.
Conclusions and implications: From our results, activation of M(2) receptors induced nNOS and eNOS expression and activation of NOS up-regulated M(2) receptor gene expression. The signalling pathways involved included stimulation of PI turnover via PLC activation, CaM and PKC. nNOS and eNOS mediated opposing effects on the negative inotropic effect in atria, induced by stimulation of M(2) receptors. These results may contribute to a better understanding of the effects and side effects of cholinomimetic treatment in patients with cardiac neuromyopathy.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cardiac function and pathophysiology.J Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;592(15):3189-200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.270306. Epub 2014 Apr 22. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24756636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlations between neuronal nitric oxide synthase and muscarinic M3/M1 receptors in the rat retina.Exp Eye Res. 2005 Mar;80(3):391-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.09.016. Exp Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 15721621
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase activity in rat urinary bladder detrusor: participation in M3 and M4 muscarinic receptor function.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;25(3):93-100. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2005.00337.x. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15955028
-
Differential signalling pathways involved in cholinoceptor-dependent stimulation of nitric oxide isoforms in dental pulp.Int Endod J. 2007 Jul;40(7):544-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01259.x. Epub 2007 May 18. Int Endod J. 2007. PMID: 17511785
-
Regulation of expression and function of muscarinic receptors.Life Sci. 1993;52(5-6):429-32. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90298-h. Life Sci. 1993. PMID: 8441324 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in cardiac function and pathophysiology.J Physiol. 2014 Aug 1;592(15):3189-200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.270306. Epub 2014 Apr 22. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24756636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise benefits cardiovascular health in hyperlipidemia rats correlating with changes of the cardiac vagus nerve.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010 Feb;108(3):459-68. doi: 10.1007/s00421-009-1232-1. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19830451
-
Epithelium integrity is crucial for the relaxant activity of brain natriuretic peptide in human isolated bronchi.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(8):1740-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01339.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21410689 Free PMC article.
-
Peculiarities of the Acetylcholine Action on the Contractile Function of Cardiomyocytes from the Left and Right Atria in Rats.Cells. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):3809. doi: 10.3390/cells11233809. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht C, Von Der Kammer H, Mayhaus M, Klaudiny J, Schweizer M, Nitsch RM. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors induce the expression of the immediate early growth gene CYR61. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:28929–28936. - PubMed
-
- Borda ES, Perez Leiros C, Camusso JJ, Bacman S, Sterin-Borda L. Differential cholinoceptor subtype-dependent activation of signal transduction pathways in neonatal versus adult rat atria. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53:959–967. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Ferris CD, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10976–10981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

