Functioning of patients with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy (CIAP)
- PMID: 17385078
- PMCID: PMC2794339
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-006-0501-8
Functioning of patients with chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy (CIAP)
Abstract
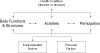
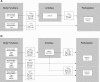
Although patients with Chronic Idiopathic Axonal Polyneuropathy (CIAP) report a slow deterioration of sensory and motor functions, the impact of this deterioration on daily functioning has not yet been investigated in detail. The first aim of this cross-sectional study involving 56 patients with CIAP was, therefore, to assess patients' functioning with use of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF). The second aim was to find determinants of walking ability, dexterity, and autonomy. Fatigue and limited walking ability were present in most patients and differed considerably. In regression models, age, muscle strength, and fatigue together explained 63% of the variance in walking ability, which by itself explained almost 50% of the variance in patients' autonomy indoors and outdoors (42% and 49%, respectively). Muscle strength and sensory function scores together explained 30% of the variance in dexterity scores, which in turn explained only 13% of the variance in autonomy indoors. The diminished autonomy of patients with CIAP might be improved by reducing fatigue, by means of training, and by improving walking ability.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/jnnp.47.5.530', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.47.5.530'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1027832', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1027832/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '6330306', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6330306/'}]}
- McLeod JG, Tuck RR, Pollard JD, Cameron J, Walsh JC (1984) Chronic polyneuropathy of undetermined cause. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:530–535 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/jnnp.56.10.1066', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.56.10.1066'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1015233', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1015233/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7691991', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7691991/'}]}
- Notermans NC, Wokke JHJ, Franssen H, van der Graaf Y, Vermeulen M, van den Berg LH, Bar PR, Jennekens FG (1993) Chronic idiopathic polyneuropathy presenting in middle or old age: a clinical and electrophysiological study of 75 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:1066–1071 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/jnnp.57.12.1525', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.57.12.1525'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1073236', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1073236/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '7798984', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7798984/'}]}
- Notermans NC, Wokke JHJ, van der Graaf Y, Franssen H, van Dijk GW, Jennekens FG (1994) Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy: a five year follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:1525–1527 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/brain/awh192', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh192'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15201191', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15201191/'}]}
- Hughes RAC, Umapathi T, Gray IA, Gregson NA, Noori M, Pannala AS, Proteggente A, Swan AV (2004) A controlled investigation of the cause of chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy. Brain 127:1723–1730 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2001) International classification of functioning, disability and health: ICF. Geneva
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

