Differential binding characteristics of native monomeric and polymeric immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) on human mesangial cells and the influence of in vitro deglycosylation of IgA1 molecules
- PMID: 17386074
- PMCID: PMC1941933
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03374.x
Differential binding characteristics of native monomeric and polymeric immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) on human mesangial cells and the influence of in vitro deglycosylation of IgA1 molecules
Abstract
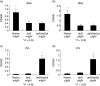
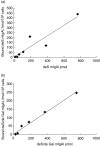
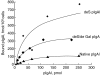
Recent studies had demonstrated that serum and mesangial immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) in patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) were polymeric and deglycosylated. The current study was to investigate the binding characteristics of monomeric and polymeric normal human IgA1 on mesangial cells and the influence of in vitro deglycosylation of IgA1 molecules. The normal human IgA1 was desialylated and degalactosylated with specific enzymes, respectively. The monomeric IgA1 (mIgA1) and polymeric IgA1 (pIgA1) were separated by Sephacryl S-300 chromatography. The binding capacities of the mIgA1 and pIgA1 to primary human mesangial cells (HMC) were evaluated by classical radioligand assay. Both the native mIgA1 and pIgA1 could bind to HMC in a dose-dependent and saturable manner. The maximal binding capacity of the native pIgA1 were significantly higher than that of the native mIgA1 (P < 0.05). However, the affinity of the native mIgA1 was almost 100 times higher than that of the native pIgA1. After deglycosylation, binding of the two deglycosylated mIgA1 to HMC could not be detected. However, the maximal binding capacities of the two deglycosylated pIgA1 to HMC were increased significantly compared with that of native pIgA1. The affinity of the two deglycosylated pIgA1 was similar to that of native pIgA1 (P > 0.05). The current study suggests differential binding characteristics of native monomeric and polymeric IgA1 on mesangial cells. Glycosylation of IgA1 molecules could significantly affect the binding of IgA1 on HMC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Increased binding of polymeric lambda-IgA to cultured human mesangial cells in IgA nephropathy.Kidney Int. 1996 Mar;49(3):839-45. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.116. Kidney Int. 1996. PMID: 8648928
-
Charge-dependent binding of polymeric IgA1 to human mesangial cells in IgA nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2001 Jan;59(1):277-85. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00489.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11135081
-
Binding capacity and pathophysiological effects of IgA1 from patients with IgA nephropathy on human glomerular mesangial cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Apr;136(1):168-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02408.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15030528 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features of IgA molecules which contribute to IgA nephropathy.J Nephrol. 1999 Mar-Apr;12(2):59-65. J Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10378660 Review.
-
Transferrin receptor engagement by polymeric IgA1 induces receptor expression and mesangial cell proliferation: role in IgA nephropathy.Contrib Nephrol. 2007;157:144-7. doi: 10.1159/000102457. Contrib Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17495453 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased plasma sVCAM-1 is associated with severity in IgA nephropathy.BMC Nephrol. 2013 Jan 22;14:21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-21. BMC Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23336423 Free PMC article.
-
Serum under-O-glycosylated IgA1 level is not correlated with glomerular IgA deposition based upon heterogeneity in the composition of immune complexes in IgA nephropathy.BMC Nephrol. 2014 Jun 13;15:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-89. BMC Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24928472 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Synergistic effect of mesangial cell-induced CXCL1 and TGF-β1 in promoting podocyte loss in IgA nephropathy.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 30;8(8):e73425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073425. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023680 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors attenuate P-aIgA1-induced cell proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis in human renal mesangial cells in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Feb;37(2):228-34. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.79. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26775659 Free PMC article.
-
The combined role of galactose-deficient IgA1 and streptococcal IgA-binding M Protein in inducing IL-6 and C3 secretion from human mesangial cells: implications for IgA nephropathy.J Immunol. 2014 Jul 1;193(1):317-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302249. Epub 2014 May 21. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24850720 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Donadio JV, Grande JP. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy: a clinical perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:1324–32. - PubMed
-
- Donadio JV, Grande JP. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:738–48. - PubMed
-
- Leung JC, Tsang AW, Chan LY, Tang SC, Lam MF, Lai KN. Size-dependent binding of IgA to HepG2, U937, and human mesangial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 2002. pp. 398–406. - PubMed
-
- Hiki Y, Tanaka A, Kokubo T, et al. Analyses of IgA1 hinge glycopeptides in IgA nephropathy by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:577–82. - PubMed
-
- Allen AC, Bailey EM, Barratt J, Buck KS, Feehally J. Analysis of IgA1 O-glycans in IgA nephropathy by fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1763–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

